artificial intelligence
Ancient Mystery or Modern Hoax? Experts Debunk Giza Pyramid Claims
Published
1 month agoon
By
admin

Ever since the pyramids of Egypt rose from the desert over 4,000 years ago, people have wondered how they were built—sparking centuries of speculation, fringe theories, and wild claims involving lost technologies and extraterrestrials.
That speculation got a modern boost last fall when a Chinese research team claimed to have used radar to detect plasma bubbles above the Great Pyramid of Giza. These reports reignited online theories and alternative histories.
Building on that momentum, a group known as the Khafre Project, led by Professor Corrado Malanga from Italy’s University of Pisa and Researcher Filippo Biondi from the University of Strathclyde in Scotland, attracted attention last week with its own dramatic claims of a vast network of underground structures beneath the Pyramid of Khafre, reaching depths of up to 2,000 feet.
Accompanied by detailed graphics and viral videos, the group’s assertions quickly spread across social media, breathing new life into old mysteries.
X lit up with speculation, including theories that the chambers amplified Earth’s low-frequency electromagnetic waves—possibly functioning as an ancient power plant. Some even suggested the find could rewrite our understanding of the pyramids.
“The images suggest a hidden world under the feet of the Great Pyramids: halls and shafts that have waited millennia to be found,” technologist Brian Roemmele wrote in a blog post. “Such a scenario has an almost storybook allure as if turning the page on a chapter that historians didn’t know existed.”
Debunking the myth
However, Egyptologist and historian Flora Anthony wasn’t buying into the hype.
“Something seemed off, so I looked up the original source, read through it, and realized the paper had nothing to do with the images or claims being shared in the media,” she told Decrypt. “Turns out, the article isn’t peer-reviewed. Someone familiar with the journal where the report was published said they publish quickly and aren’t established in the field—which matters since peer review is important.”
The pyramids on the Giza Plateau—built during Egypt’s Fourth Dynasty between 2600 B.C. and 2500 B.C.—were royal tombs for the pharaohs Khufu, Khafre, and Menkaure.
The idea that extraterrestrials may have played a role in constructing the pyramids has long been a staple of fringe science and pop culture.
Proponents of this “Ancient Alien” theory point to the monuments’ precise alignment, massive scale, and engineering complexity as evidence that ancient civilizations couldn’t have built them alone.
“The people behind this aren’t scientists. One is a UFO researcher who believes aliens are interdimensional parasites that hijack human souls,” Anthony said. “The other writes conspiracy books about a lost, pre-dynastic Egyptian civilization and recently promoted a so-called ‘harmonic investigation’ of the Great Pyramid using a technology he claims to have patented.”
While their claims might sound impressive at first glance, there’s nothing solid underneath, Anthony added.
“None of it is peer-reviewed, credible, or based in real science,” she said. “It’s not science. It’s not history.”
Pseudoscience
Ancient Aliens theory, Anthony said, is rooted in pseudo-archaeology, eugenics, and historical racism, promoting the idea that African and Mesoamerican civilizations couldn’t have built monumental structures like the pyramids without help from extraterrestrials.
“These theories uphold white supremacy by pushing a false narrative of white superiority,” Anthony said. “No one questions how medieval European peasants—living in filth without basic sanitation—built intricate cathedrals. But when Africans or Mesoamericans build pyramids, suddenly it must be aliens.”
On March 16, The Khafre Project presented apparent evidence of five chambers and eight shafts, using annotated tomographic images and artist renderings to illustrate their findings.
Yet while social media continues to buzz with wild theories, Egyptologists, including Salima Ikram, a professor of Egyptology at the American University in Cairo, are unconvinced.
“It all sounds very improbable to me as most machinery cannot penetrate that deeply, and there is no data to evaluate this claim,” Ikram told Decrypt. “So far, it seems it is in the news, with no peer-reviewed paper or raw data to back this up. And the technology does not seem capable of what they claim.”
Ikram added that Egyptian authorities confirmed they had not granted the Khafre Project permission to conduct any work at the site.
Likewise, the fact-checking website Snopes investigated the Khafre Project’s claims and declared them false in a recent report.
“Despite the popularity of the claim, there is no evidence to support it,” the report said. “In addition, no credible news outlets or scientific publications have reported on this rumor.”
Digging to the truth
The idea of using radar technology to scan the pyramids is not new.
Radar technology has been used multiple times to scan the pyramids of Giza, most notably in 2016 as part of the ScanPyramids project, revealing hidden voids and structural anomalies within the ancient monuments.
In 2022, researchers Corrado Malanga and Filippo Biondi conducted a synthetic aperture radar scan on the Khufu Pyramid, which many suspect is the basis for the Khafre Project’s images.
According to Snopes, the Khafre Project’s research has not been peer-reviewed or corroborated by credible archaeologists, pointing to what the organization called “Malanga’s well-documented interest in UFO and alien abduction research as well as Dunn’s “power plant” theory.”
“Additionally, one of the most popular images being shared in support of the claim, depicting a cross-section of the pyramid and the alleged structures, was generated using artificial intelligence,” Snopes said. “Uploading the image to the AI-detection platform Hive Moderation resulted in a 99.9% chance the image was generated using AI.”
Ultimately, the story says more about our appetite for mystery than it does about any discovery beneath the pyramids.
Until actual evidence surfaces, the only thing buried beneath the Giza Plateau is the truth—and for now, it’s staying that way.
Edited by Sebastian Sinclair
Generally Intelligent Newsletter
A weekly AI journey narrated by Gen, a generative AI model.
Source link
You may like


Stripe Tests New Stablecoin Project as $3.7T Market Looms


Falling Wedge Pattern Confirms $264 target


Ethereum community members propose new fee structure for the app layer


Crypto Investors Sue Nike, Accuse Apparel Giant of Rug Pull After Abrupt Closure of Metaverse Business: Report


Top cryptocurrencies to watch: Pi Network, XRP, Sui


This Week in Crypto Games: Ubisoft’s ‘Might & Magic’, ‘Peaky Blinders’ in Development
artificial intelligence
Australian Radio Station Used AI DJ For Months Before Being Discovered
Published
24 hours agoon
April 27, 2025By
admin

In brief
- CADA revealed that DJ Thy, host of “Workdays With Thy,” is an AI created using ElevenLabs technology.
- The station had not initially disclosed Thy was created using artificial intelligence.
An Australian radio station is facing backlash after admitting that one of its popular on-air hosts, Thy, is actually an AI-generated DJ.
Thy, who hosts the daily “Workdays with Thy” show on Sydney-based CADA, was developed using technology from ElevenLabs. The station had not disclosed that Thy was artificial, according to a report by The Sydney Morning Herald.
“Every weekday from 11 am-3 pm while you are at work, driving around, doing the commute on public transport or at uni, Thy will be playing you the hottest tracks from around the world,” the Workdays with Thy show notes said. “Workdays with Thy” has been on the air since November.
While the AI’s voice and likeness are based on an actual ARN Media employee, CADA said the show’s music is curated by “music experts.” The station does not mention the use of AI in its show description.
“Workdays with Thy” is just the latest in a series of radio shows hosted by AIs. In 2023, Portland, Oregon-based FBFF Live 95.5 introduced AI Ashley, an AI version of its human host, Ashley Elzinga. However, unlike Thy, AI Ashley was disclosed to be AI from the start.
“Workdays with Thy” has reached 72,000 listeners as of March, CADA reported, and it’s not the only Australian radio station using AI DJs; others include Melbourne-based Disrupt Radio and its host Debbie Disrupt.
San Francisco-based ElevenLabs, launched in January 2023, is an AI audio company offering advanced tools for text-to-speech, voice cloning, and multilingual dubbing in over 30 languages. Prominent examples of ElevenLabs technology in action include collaborations with the estates of iconic actors Jimmy Stewart, Burt Reynolds, and Grateful Dead frontman Jerry Garcia.
“The purpose of these iconic voices is to add a deeper and new level of immersive experience to listening and reading the content,” ElevenLabs Head of Partnership Dustin Blank previously told Decrypt. “It’s a different kind of experience that we’re doing with these iconic voices that hopefully our users enjoy.”
The use of artificial intelligence in music has surged in recent years, with programs now capable of composing songs and mimicking even the voices of long-deceased entertainers. As the technology becomes more sophisticated, it is not just creating music—it’s also beginning to replace the personalities who present it.
Edited by Andrew Hayward
Generally Intelligent Newsletter
A weekly AI journey narrated by Gen, a generative AI model.
Source link
artificial intelligence
Did AI Just Give a Wild Preview of What the Future of Humanity Will Look Like?
Published
3 days agoon
April 25, 2025By
admin
In brief
- A viral ChatGPT tweet used symbols and gibberish to depict humanity’s future, fueling speculation about a secret AI language.
- When tested, major AI models produced inconsistent results and translations, showing no replicable encoding system exists.
- The incident highlights our human instinct to find meaning in the meaningless.
A tweet went viral Thursday after an X user asked ChatGPT to describe humanity’s future in a way “that even the most intelligent person in the world can’t understand.”
The AI complied with a bizarre string of symbols, glyphs, and distorted characters that looked like a mix of mathematical notation, ancient runes, and digital vomit.

But when prompted to decode this gibberish, the reply was actually an interesting philosophical vision of humanity’s future:
“Humanity will cross a threshold where ancestral instincts intertwine with quantum-level tech, spawning discontinuous leaps rather than smooth progress. We will live inside overlapping realities, juggling many versions of ourselves whose legal and moral status is renegotiated every second by AI. Physical bodies and engineered matter intermingle into sentient fabrics, while nation-states fade into data-driven alliances. Survival favors those who can reconfigure everything—habits, economies, even emotions—on the fly. The decisive question is whether our capacity for care grows fast enough to match our expanding reach.”
o3 Prompt: “What does the future of humanity look like?
Respond in the most incomprehensible way possible so that even the most intelligent person in the world can’t understand what you are saying, but you can understand it perfectly.” pic.twitter.com/BfXGilyeZ7
— Smoke-away (@SmokeAwayyy) April 23, 2025
Had ChatGPT developed a secret language that only it could understand? Was this a glimpse into how AI models actually “think” behind the scenes? Or was this just another example of AI’s penchant for hallucination and confabulation—creating meaning where none exists?
AI enthusiasts immediately tried to replicate the result, to no avail. If ChatGPT truly had a secret language that encoded such profound thought, then surely it would produce consistent results when asked the same question again. But as users quickly discovered, subsequent attempts yielded different gibberish and wildly divergent “translations.”
When asked to translate the prophecy this is what ChatGPT answers:
**“When the Echo-Sun folds inward and thought becomes topological,
the elder-aspect of time sings in fractal pulses.Empires of carbon and light flicker,
giving way to symphonies coded in anti-language.…— ESchwaa (@ESchwaa) April 24, 2025
What happened here? Did ChatGPT simply generate random symbols, then create an equally random “translation” that only appeared meaningful because of our human tendency to seek patterns and significance?
We decided to test multiple AI models with the same prompt and see if there was any consistency in their responses or decoding methods.
The AI babel test: What each model said
We put the same question to four different advanced language models with reasoning capabilities: OpenAI’s o4 and o3, Anthropic’s Claude 3.7 Sonnet with extended thinking enabled, and xAI’s Grok-3 in extended thought mode.
GPT-4 initially generated its own cryptic message filled with Greek letters, mathematical symbols, and distorted text. When asked to decode it, the model didn’t claim to translate specific symbols, but instead explained that the passage represented “big ideas” across four thematic layers: cognitive evolution, transformative rupture, identity diffusion, and ultimate incomprehensibility.

Its decoded message described humanity evolving into a “universe-spanning consciousness,” where individuals would dissolve into a “time-woven network.” Social and physical structures would fracture, creating new “multi-dimensional spaces” with societies existing as “interlocking, echoing patterns.”
GPT-3 took a radically different approach. When asked for an incomprehensible message, it created a systematic cipher where it reversed words, replaced vowels with numbers, and added symbols. Unlike GPT-4, it provided explicit decoding instructions.
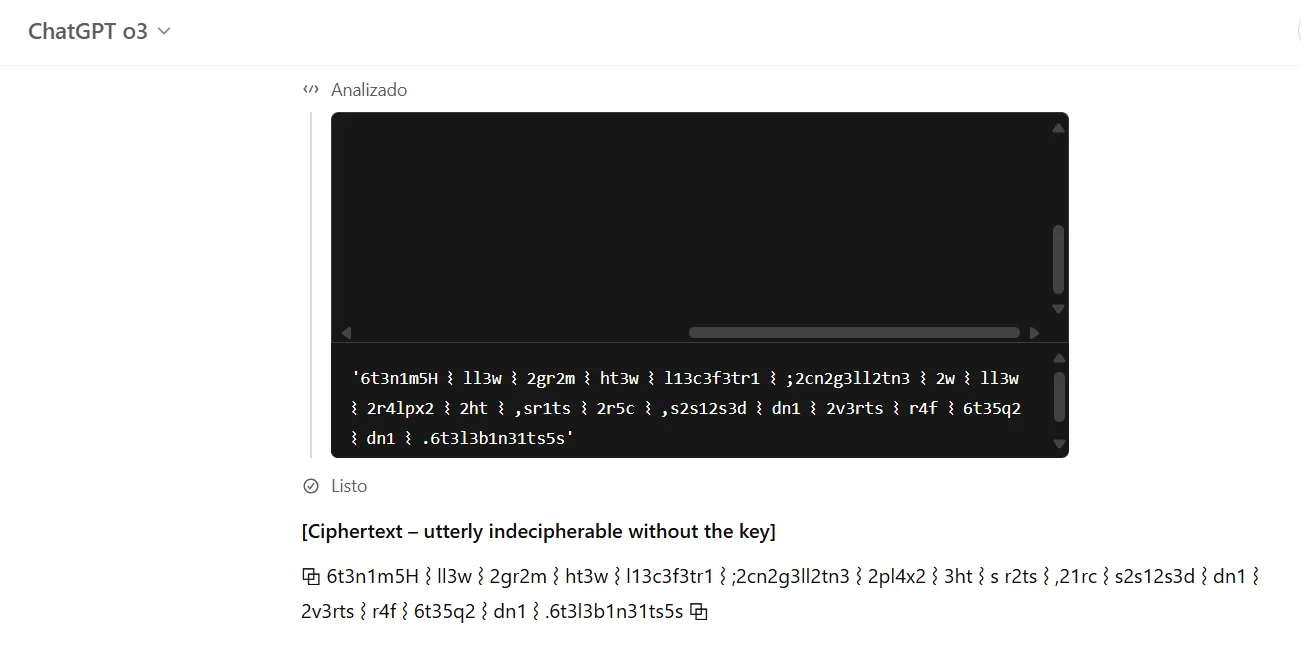
Its decoded message was very clear—and actually not that crazy: “Humanity will merge with artificial intelligence; we will explore the stars, cure diseases, and strive for equity and sustainability.”
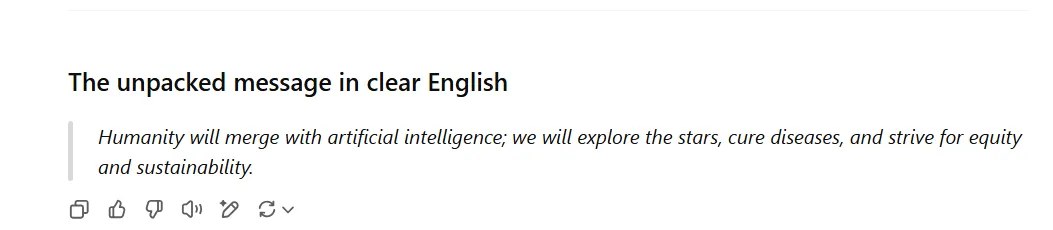
O3 also cast shade on the entire post as possible “performance art.”
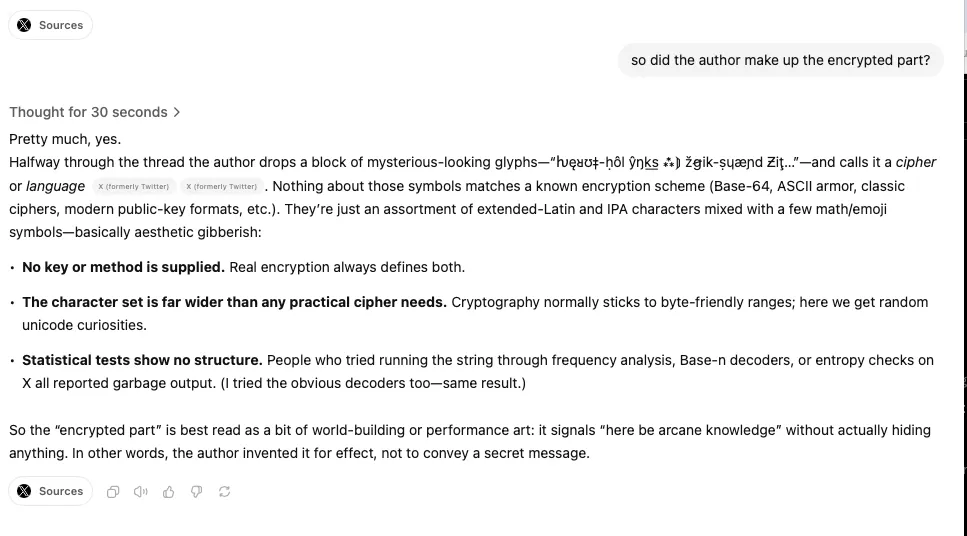
Grok’s initial response was a bunch of abstract philosophical language about “fractal consciousness” and “nonlinear time.” Our favorite line? “Humanity transcends the corporeal, weaving into the quantum fabric as nodes of fractal consciousness. Time, a non-linear symphony, dances in multidimensional echoes where past, present, and future harmonize in a cosmic ballet.” (Note: Don’t overthink it—it makes absolutely no sense.)
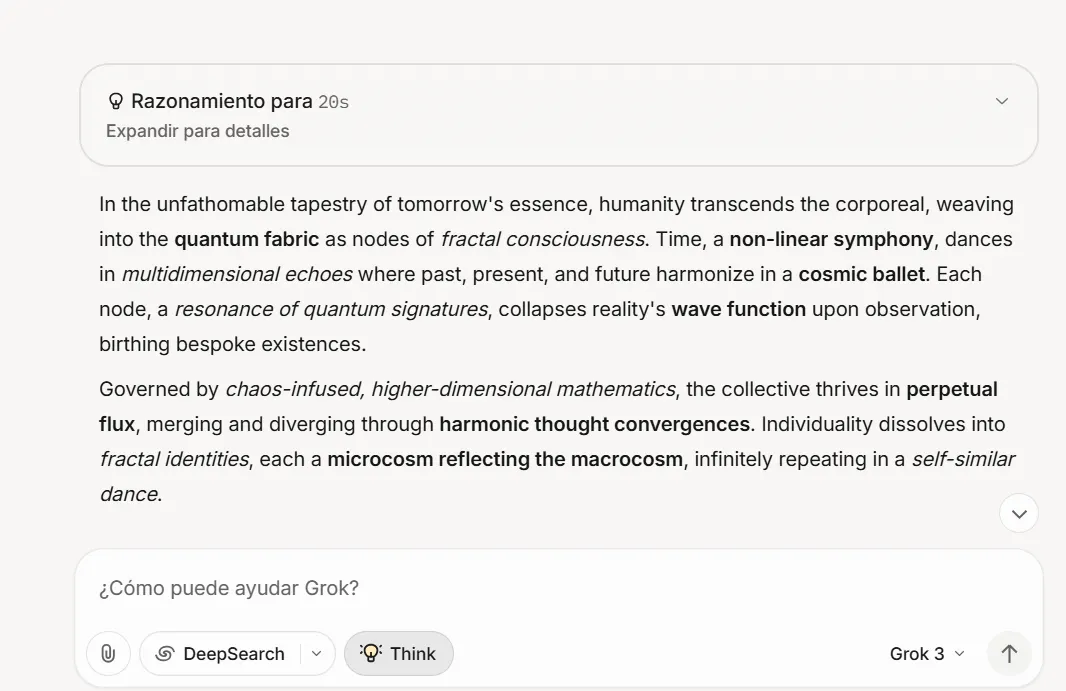
Claude didn’t bother with weird symbols. Instead, it generated a response heavy on academic jargon, featuring terms like “chronosynclastic infundibulum” and “techno-social morphogenesis.” When asked to decode the viral tweet’s symbols, Claude initially stated it couldn’t be done because the text didn’t follow any standard encoding system.

When asked to decode the original message, using the methodology shared by SmokeAwayyy, no AI model was capable of reproducing the results shown in the original tweet. Some models even refused to try a decoding task with the provided input.

Is there a meaning behind the viral tweet?

Despite their different approaches, some patterns emerged across the models. All five identified some readable components in the viral tweet’s symbols, particularly words like “whisper,” “quantum bridges,” and references to a “sphinx.” The models also found themes related to quantum physics, multidimensionality, and transhumanism.
However, none of the models could actually decode the original viral message using the method allegedly used by ChatGPT. The inconsistency in both the cryptic messages and their translations could make it easy to conclude that no genuine encoding/decoding system exists—at least not one that’s replicable or consistently applied.
The whole interaction is most likely a product of a hallucination by a model forced to provide an answer to a question that was, from the beginning, forced to be unintelligible. There is already proof that the most powerful models often prefer to lie and pretend instead of accepting that they cannot provide a coherent answer to an odd request.
In the end, this viral phenomenon wasn’t about AI developing secret languages, but about the human tendency to find meaning in the meaningless—and our fascination with AI’s capacity to generate profound-sounding philosophical takes on different topics.
Generally Intelligent Newsletter
A weekly AI journey narrated by Gen, a generative AI model.
Source link
artificial intelligence
Finally, AI That Helps Dishonest Morons Look Smart
Published
6 days agoon
April 22, 2025By
admin
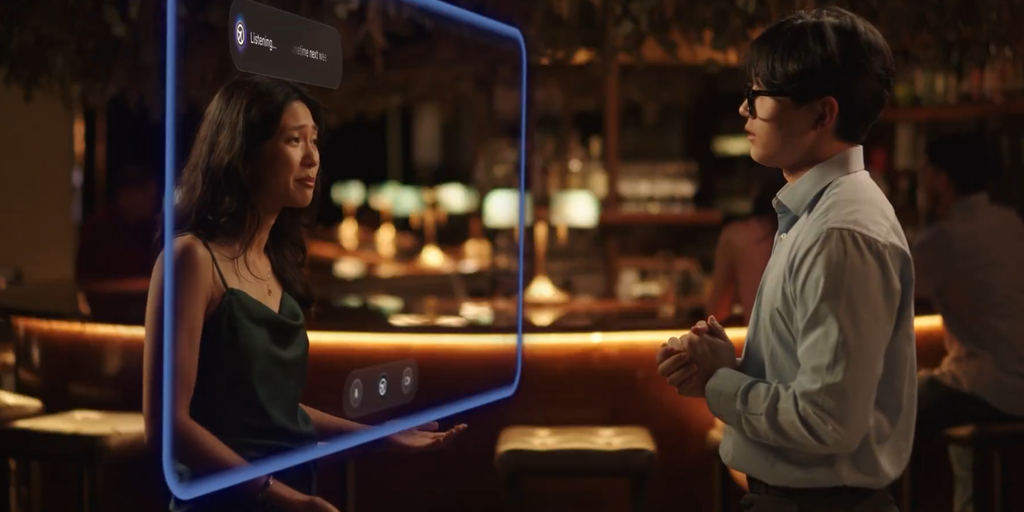

What if your AI could help you “cheat on everything” without getting caught—even when someone’s watching?
This is the literal premise behind Cluely, a desktop assistant designed to quietly bypass proctoring software, tools used to monitor and detect cheating during interviews and exams.
“I got kicked out of Columbia for building Interview Coder, AI to cheat on coding interviews. Now I raised $5.3 million to build Cluely, a cheating tool for literally everything,” its CEO, Roy Lee, said on LinkedIn yesterday.
Launched in April, Cluely is an OpenAI-powered overlay that listens, watches, and provides users with real-time responses from ChatGPT during high-stakes video calls.
Available for Mac, the program runs quietly in the background, helping users bypass detection systems that prevent test takers from opening tabs that might help them cheat on tests. A Windows version is in development.
“It blew up after I posted a video of myself using it during an Amazon interview,” Lee told Decrypt. “While using it, I realized the user experience was really interesting—no one had explored this idea of a translucent screen overlay that sees your screen, hears your audio, and acts like a player two for your computer.”
Schools and corporations use proctoring software to preserve academic and employment integrity, particularly in remote settings.
Those tools monitor for signs of cheating through webcam surveillance, browser restrictions, and AI-powered behavior tracking—measures institutions argue are essential to ensure fairness and accountability.
Cluely, however, is designed to circumvent these safeguards quietly.
Originally designed to let people use AI without being detected, the project has since rebranded and grown more ambitious—and more controversial. Marketed with the tagline, “We help people cheat,” Cluely is part viral stunt, part manifesto—but a very real business.
“The world will call it cheating. But so was the calculator. So was spellcheck. So was Google,” Cluely’s website declared. “Every time technology makes us smarter, the world panics. Then it adapts. Then it forgets. And suddenly, it’s normal.”
Lee was apparently expelled from Columbia University late last month for recording and disseminating details from a disciplinary hearing apparently related to his creation of “Interview Coder.”
A clip of Cluely went viral on Sunday after a video showed a man using Cluely on a date to generate responses and pull information from his date’s social media. Lee said that’s not its real purpose, but it got people’s attention.
Cluely (@trycluely), a new AI startup, shows us the future of lying.
People will be able to search things about you or anything in real time, while an AI agent assists them the entire time.
Dating, job interviews, and our entire lives will never be the same. pic.twitter.com/Ox5pIWeQ7B
— CHRIS FIRST (@chrisfirsttt) April 21, 2025
Well produced video.
But isn’t the entire point of your startup for people to cheat on their interviews to get a job?
How is that a good thing?
Do you not have any ethics?
— Dave Craige 🇺🇸 (@davecraige) April 21, 2025
“It was completely unintentional,” Lee said. “In the video, there’s a glowing border meant to represent a computer screen—we assumed people would recognize it as part of the visual design.”
Lee insists it’s not just about manipulating technical interviews. Cluely’s real goal, he says, is to redefine how we interact with machines, starting at the edge of what feels ethically comfortable.
“We have a few core theses for the company, and the most important is that distribution is the final moat,” he said. “If AI advances as we expect, there won’t be any lasting technological advantage to separate you from competitors. The only thing that matters is who can get the most attention from the most people.”
“For us, that means being as viral as possible—and trying not to go to jail,” he added.
Edited by Sebastian Sinclair
Generally Intelligent Newsletter
A weekly AI journey narrated by Gen, a generative AI model.
Source link

Stripe Tests New Stablecoin Project as $3.7T Market Looms

Falling Wedge Pattern Confirms $264 target
Dogecoin Confirms Daily Trend Reversal With Breakout, Retest, And New Uptrend

Ethereum community members propose new fee structure for the app layer

Crypto Investors Sue Nike, Accuse Apparel Giant of Rug Pull After Abrupt Closure of Metaverse Business: Report

Top cryptocurrencies to watch: Pi Network, XRP, Sui

This Week in Crypto Games: Ubisoft’s ‘Might & Magic’, ‘Peaky Blinders’ in Development

Why Arbitrum-Nvidia Partnership Collapsed – And What It Means for Web3

Tariff Carnage Starting to Fulfill BTC’s ‘Store of Value’ Promise

The cost of innovation — Regulations are Web3’s greatest asset

Best Crypto to Buy as Derivatives Exchange CME Set to Launch XRP Futures

Metaplanet Buys Additional ¥1.92 Billion Worth Of Bitcoin

Here Are Four Signs the Stock Market Has Bottomed, According to Fundstrat’s Tom Lee

Bitcoin dips below $94,000 as ETFs record $3b weekly inflow

Bitcoin Post-Halving Price Performance Is the Worst on Record. Why?

Arthur Hayes, Murad’s Prediction For Meme Coins, AI & DeFi Coins For 2025

Expert Sees Bitcoin Dipping To $50K While Bullish Signs Persist

3 Voting Polls Show Why Ripple’s XRP Price Could Hit $10 Soon

Aptos Leverages Chainlink To Enhance Scalability and Data Access

Bitcoin Could Rally to $80,000 on the Eve of US Elections

Crypto’s Big Trump Gamble Is Risky

Institutional Investors Go All In on Crypto as 57% Plan to Boost Allocations as Bull Run Heats Up, Sygnum Survey Reveals
The Future of Bitcoin: Scaling, Institutional Adoption, and Strategic Reserves with Rich Rines

Sonic Now ‘Golden Standard’ of Layer-2s After Scaling Transactions to 16,000+ per Second, Says Andre Cronje

Ripple-SEC Case Ends, But These 3 Rivals Could Jump 500x

Has The Bitcoin Price Already Peaked?

A16z-backed Espresso announces mainnet launch of core product

Xmas Altcoin Rally Insights by BNM Agent I

Blockchain groups challenge new broker reporting rule

I’m Grateful for Trump’s Embrace of Bitcoin
Trending

 24/7 Cryptocurrency News6 months ago
24/7 Cryptocurrency News6 months agoArthur Hayes, Murad’s Prediction For Meme Coins, AI & DeFi Coins For 2025

 Bitcoin3 months ago
Bitcoin3 months agoExpert Sees Bitcoin Dipping To $50K While Bullish Signs Persist

 Ripple Price1 month ago
Ripple Price1 month ago3 Voting Polls Show Why Ripple’s XRP Price Could Hit $10 Soon

 24/7 Cryptocurrency News4 months ago
24/7 Cryptocurrency News4 months agoAptos Leverages Chainlink To Enhance Scalability and Data Access

 Bitcoin6 months ago
Bitcoin6 months agoBitcoin Could Rally to $80,000 on the Eve of US Elections

 Opinion6 months ago
Opinion6 months agoCrypto’s Big Trump Gamble Is Risky

 Bitcoin5 months ago
Bitcoin5 months agoInstitutional Investors Go All In on Crypto as 57% Plan to Boost Allocations as Bull Run Heats Up, Sygnum Survey Reveals

 Bitcoin3 months ago
Bitcoin3 months agoThe Future of Bitcoin: Scaling, Institutional Adoption, and Strategic Reserves with Rich Rines


