artificial intelligence
How the US Military Says Its Billion Dollar AI Gamble Will Pay Off
Published
5 months agoon
By
admin

War is more profitable than peace, and AI developers are eager to capitalize by offering the U.S. Department of Defense various generative AI tools for the battlefields of the future.
The latest evidence of this trend came last week when Claude AI developer Anthropic announced that it was partnering with military contractor Palantir and Amazon Web Services (AWS) to provide U.S. intelligence and the Pentagon access to Claude 3 and 3.5.
Anthropic said Claude will give U.S. defense and intelligence agencies powerful tools for rapid data processing and analysis, allowing the military to perform faster operations.
Experts say these partnerships allow the Department of Defense to quickly adopt advanced AI technologies without needing to develop them internally.
“As with many other technologies, the commercial marketplace always moves faster and integrates more rapidly than the government can,” retired U.S. Navy Rear Admiral Chris Becker told Decrypt in an interview. “If you look at how SpaceX went from an idea to implementing a launch and recovery of a booster at sea, the government might still be considering initial design reviews in that same period.”
Becker, a former Commander of the Naval Information Warfare Systems Command, noted that integrating advanced technology initially designed for government and military purposes into public use is nothing new.
“The internet began as a defense research initiative before becoming available to the public, where it’s now a basic expectation,” Becker said.
Anthropic is only the latest AI developer to offer its technology to the U.S. government.
Following the Biden Administration’s memorandum in October on advancing U.S. leadership in AI, ChatGPT developer OpenAI expressed support for U.S. and allied efforts to develop AI aligned with “democratic values.” More recently, Meta also announced it would make its open-source Llama AI available to the Department of Defense and other U.S. agencies to support national security.
During Axios’ Future of Defense event in July, retired Army General Mark Milley noted advances in artificial intelligence and robotics will likely make AI-powered robots a larger part of future military operations.
“Ten to fifteen years from now, my guess is a third, maybe 25% to a third of the U.S. military will be robotic,” Milley said.
In anticipation of AI’s pivotal role in future conflicts, the DoD’s 2025 budget requests $143.2 billion for Research, Development, Test, and Evaluation, including $1.8 billion specifically allocated to AI and machine learning projects.
Protecting the U.S. and its allies is a priority. Still, Dr. Benjamin Harvey, CEO of AI Squared, noted that government partnerships also provide AI companies with stable revenue, early problem-solving, and a role in shaping future regulations.
“AI developers want to leverage federal government use cases as learning opportunities to understand real-world challenges unique to this sector,” Harvey told Decrypt. “This experience gives them an edge in anticipating issues that might emerge in the private sector over the next five to 10 years.
He continued: “It also positions them to proactively shape governance, compliance policies, and procedures, helping them stay ahead of the curve in policy development and regulatory alignment.”
Harvey, who previously served as chief of operations data science for the U.S. National Security Agency, also said another reason developers look to make deals with government entities is to establish themselves as essential to the government’s growing AI needs.
With billions of dollars earmarked for AI and machine learning, the Pentagon is investing heavily in advancing America’s military capabilities, aiming to use the rapid development of AI technologies to its advantage.
While the public may envision AI’s role in the military as involving autonomous, weaponized robots advancing across futuristic battlefields, experts say that the reality is far less dramatic and more focused on data.
“In the military context, we’re mostly seeing highly advanced autonomy and elements of classical machine learning, where machines aid in decision-making, but this does not typically involve decisions to release weapons,” Kratos Defense President of Unmanned Systems Division, Steve Finley, told Decrypt. “AI substantially accelerates data collection and analysis to form decisions and conclusions.”
Founded in 1994, San Diego-based Kratos Defense has partnered extensively with the U.S. military, particularly the Air Force and Marines, to develop advanced unmanned systems like the Valkyrie fighter jet. According to Finley, keeping humans in the decision-making loop is critical to preventing the feared “Terminator” scenario from taking place.
“If a weapon is involved or a maneuver risks human life, a human decision-maker is always in the loop,” Finley said. “There’s always a safeguard—a ‘stop’ or ‘hold’—for any weapon release or critical maneuver.”
Despite how far generative AI has come since the launch of ChatGPT, experts, including author and scientist Gary Marcus, say current limitations of AI models put the real effectiveness of the technology in doubt.
“Businesses have found that large language models are not particularly reliable,” Marcus told Decrypt. “They hallucinate, make boneheaded mistakes, and that limits their real applicability. You would not want something that hallucinates to be plotting your military strategy.”
Known for critiquing overhyped AI claims, Marcus is a cognitive scientist, AI researcher, and author of six books on artificial intelligence. In regards to the dreaded “Terminator” scenario, and echoing Kratos Defense’s executive, Marcus also emphasized that fully autonomous robots powered by AI would be a mistake.
“It would be stupid to hook them up for warfare without humans in the loop, especially considering their current clear lack of reliability,” Marcus said. “It concerns me that many people have been seduced by these kinds of AI systems and not come to grips with the reality of their reliability.”
As Marcus explained, many in the AI field hold the belief that simply feeding AI systems more data and computational power would continually enhance their capabilities—a notion he described as a “fantasy.”
“In the last weeks, there have been rumors from multiple companies that the so-called scaling laws have run out, and there’s a period of diminishing returns,” Marcus added. “So I don’t think the military should realistically expect that all these problems are going to be solved. These systems probably aren’t going to be reliable, and you don’t want to be using unreliable systems in war.”
Edited by Josh Quittner and Sebastian Sinclair
Generally Intelligent Newsletter
A weekly AI journey narrated by Gen, a generative AI model.
Source link
You may like


Apple Delists 14 Crypto Apps in South Korea Including KuCoin and MEXC Exchanges Amid Regulatory Crackdown


Athens Exchange Group eyes first onchain order book via Sui


Futureverse Acquires Candy Digital, Taps DC Comics and Netflix IP to Boost Metaverse Strategy


Court Grants Ripple And SEC’s Joint Motion To Suspend Appeal


AVAX Falls 2.1% as Nearly All Assets Trade Lower


What is a VTuber, and how do you become one in 2025?
artificial intelligence
OpenAI Releases GPT-4.1: Why This Super-Powered AI Model Will Kill GPT-4.5
Published
2 days agoon
April 14, 2025By
admin
OpenAI unveiled GPT-4.1 on Monday, a trio of new AI models with context windows of up to one million tokens—enough to process entire codebases or small novels in one go. The lineup includes standard GPT-4.1, Mini, and Nano variants, all targeting developers.
The company’s latest offering comes just weeks after releasing GPT-4.5, creating a timeline that makes about as much sense as the release order of the Star Wars movies. “The decision to name these 4.1 was intentional. I mean, it’s not just that we’re bad at naming,” OpenAI product lead Kevin Weil said during the announcement—but we are still trying to find out what those intentions were.
GPT-4.1 shows pretty interesting capabilities. According to OpenAI, it achieved 55% accuracy on the SWEBench coding benchmark (up from GPT-4o’s 33%) while costing 26% less. The new Nano variant, billed as the company’s “smallest, fastest, cheapest model ever,” runs at just 12 cents per million tokens.
Also, OpenAI won’t upcharge for processing massive documents and actually using the one million token context. “There is no pricing bump for long context,” Kevin emphasized.
The new models show impressive performance improvements. In a live demonstration, GPT-4.1 generated a complete web application that could analyze a 450,000-token NASA server log file from 1995. openAI claims the model passes this test with nearly 100% accuracy even at million tokens of context.
Michelle, OpenAI’s post-training research lead, also showcased the models’ enhanced instruction-following abilities. “The model follows all your instructions to the tea,” she said, as GPT-4.1 dutifully adhered to complex formatting requirements without the usual AI tendency to “creatively interpret” directions.
How Not to Count: OpenAI’s Guide to Naming Models
The release of GPT-4.1 after GPT-4.5 feels like watching someone count “5, 6, 4, 7” with a straight face. It’s the latest chapter in OpenAI’s bizarre versioning saga.
After releasing GPT-4 it upgraded the model with multimodal capabilities. The company decided to call that new model GPT-4o (“o” for “omni”), a name that could be also be read as “four zero” depending on the font you use
Then, OpenAI introduced a reasoning-focused model that was just called “o.” But don’t confuse OpenAI’s GPT-4o with OpenAI’s o because they are not the same. Nobody knows why they picked this name, but as a general rule of thumb, GPT-4o was a “normal” LLM whereas OpenAI o1 was a reasoning model.
A few months after the release of OpenAI o1, came OpenAI o3.
But what about o2?—Well, that model never existed.
“You would think logically (our new model) maybe should have been called o2, but out of respect to our friends at Telefonica—and in the grand tradition of open AI being really truly bad at names—it’s going to be called o3,” Sam Altman said during the model’s announcement.
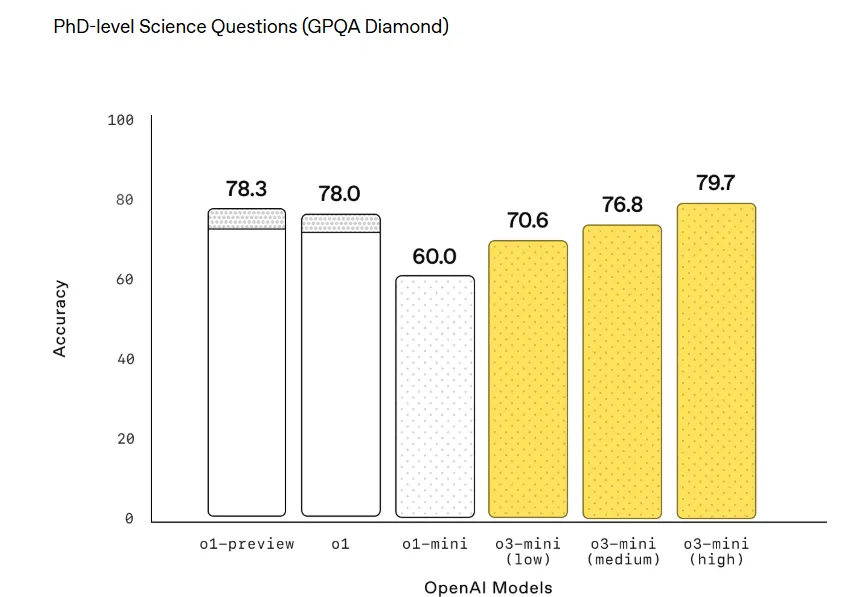
The lineup further fragments with variants like the normal o3 and a smaller more efficient version called o3 mini. However, they also released a model named “OpenAI o3 mini-high” which puts two absolute antonyms next to each other because AI can do miraculous things.In essence, OpenAI o3 mini-high is a more powerful version than o3 mini, but not as powerful as OpenAI o3—which is referenced in a single chart by Openai as “o3 (Medium),” as it should be. Right now ChatGPT users can select either OpenAI o3 mini or OpenAI o3 mini high. The normal version is nowhere to be found.
Also, we don’t want to confuse you anymore, but OpenAI already announced plans to release o4 soon. But, of course, don’t confuse o4 with 4o because they are absolutely not the same: o4 reasons—4o does not.
Now, let’s go back to the newly announced GPT-4.1. The model is so good, it is going to kill GPT-4.5 soon, making that model the shortest living LLM in the history of ChatGPT. “We’re announcing that we’re going to be deprecating GPT-4.5 in the API,” Kevin declared, giving developers a three-month deadline to switch. “We really do need those GPUs back,” he added, confirming that even OpenAI can’t escape the silicon shortage that’s plaguing the industry.
At this rate, we’re bound to see GPT-π or GPT-4.√2 before the year ends—but hey, at least they get better with time, no matter the names.
The models are already available via API and in OpenAI’s playground, and won’t be available in the user-friendly ChatGPT UI—at least not yet.
Edited by James Rubin
Generally Intelligent Newsletter
A weekly AI journey narrated by Gen, a generative AI model.
Source link
artificial intelligence
Where Top VCs Think Crypto x AI Is Headed Next
Published
3 days agoon
April 13, 2025By
admin

The proliferation of mainstream artificial intelligence (AI) tools in the last couple of years has stirred the crypto and blockchain industry to explore decentralized alternatives to Big Tech products.
The synergy between AI and blockchain is built on addressing the risk of centralized ownership and access to data that powers AI. The theory goes that decentralization can mitigate against the entire AI economy being powered by the data owned by a few tech behemoths like Alphabet (GOOG), Amazon (AMZN), Microsoft (MSFT), Alibaba (9988) and Tencent (0700).
It is unclear as yet whether or not this will prove to be a significant problem at all, much less whether the blockchain industry will be able to solve it. What is clear, however, is that crypto venture capitalists (VCs) are willing to spend millions of dollars finding out. Decentralized AI has thus far attracted $917 million in VC and private equity money, according to startup deal platform Tracxn.
The question remains whether the trend of investing in blockchain-based AI is still built on hype or has now transcended to being the real deal.
Blockchain investment company Theta Capital described AI x crypto as “the inevitable backbone of AI,” in a recent “Satellite View” report, which explored insights and outlooks from the sector’s prominent investors.
AI agents
“No trend stands out more than the intersection of AI and crypto,” the report said, using the examples of AI agents trading on blockchains and even launching tokens.
This may appear to be a more sophisticated form of speculation for degens, but Theta argues it’s a route to tackling some of AI’s problems that only crypto can solve.
“Crypto wallets enable the participation of autonomous agents in financial markets,” according to the report. “Decentralized token networks are bootstrapping the supply side of key AI infrastructure for compute, data and energy.”
The report’s conclusion is far from being hype and speculation; AI x crypto is “the new meta.” Meta is short for “metagame,” a term borrowed from gaming referring to the dominant way of playing with regard to characters, strategies or moves based on the competitive landscape.
Decentralized AI
Alex Pack, managing partner of blockchain venture capital firm Hack VC, described Web3 AI as “the biggest source of alpha in investing today,” in the “Satellite View” report.
Hack VC has dedicated 41% of its latest fund to Web3 AI, according to the report, in which it sees the main challenge as building a decentralized alternative to the AI economy.
“AI’s rapid evolution is creating massive efficiencies, but also increasing centralization,” Pack said.
“The intersection of crypto and AI is by far the biggest investment opportunity in the space, offering an open, decentralized alternative.”
One of Hack VC’s most prominent portfolio companies is Grass, which encourages users to participate in AI networks by offering up their unused internet bandwidth in return for tokens.
This is designed as an alternative to large firms installing software code into apps in order to scrape their users’ data.
“Users unwittingly donate their bandwidth without compensation,” Grass founder Andrej Radonjic said in Theta’s report.
“Grass provides an alternative [by] forming a massive opt-in, peer-to-peer network able to produce high-quality data at the scale of Google and Microsoft.”
The dreaded AI “takeover”
Decentralized AI presents risks for investors, Theta concedes. It could lead to the proliferation of all the least desirable facets of the internet as it already exists: putrid online discourse, spam emails or vapid social media content in the form of blogs, videos or memes. In the crypto world, an example of this may be the creation of meme tokens. The questionable endorsements, the wash trading and the pump and dumps can all be handled by AI engines even more efficiently than humans.
Some VCs see blockchain as the basis for mitigation. Olaf Carlson-Wee, CEO and founder of Polychain, provided the examples of proof-of-humanity mechanisms to verify that users are human and disincentivizing spam through micropayments or spam.
“If sending an email costs $0.01, it would destroy the economics of spam while remaining affordable for average users,” he said in the report.
With blockchain possibly providing some of these safeguards, Carlson-Wee believes AI will underpin digital and financial systems, as they could outperform humans in markets. This reality, he claims, would be gladly accepted, as opposed to dreaded as some sort of bleak dystopia.
“Over time, AI systems will evolve into long-term capital allocators, predicting trends and opportunities years into the future, [which] humans will entrust their funds to, because of the superior ability to make data-driven decisions,” Carlson-Wee said.
“The AI takeover won’t be a war we lose – it will be a suggestion we agree to,” he concluded.
Source link
artificial intelligence
How a Philosopher Who Criticized Trump and Musk Turned Out to Be an AI Experiment
Published
4 days agoon
April 12, 2025By
admin

Jianwei Xun, the supposed Hong Kong philosopher whose book “Hypnocracy” claims Elon Musk and President Donald Trump use utopian promises and empty language, never really existed, at least not physically.
Instead, the acclaimed author was a “collaborative” creation between Andrea Colamedici, an Italian publisher, and two AI tools – Claude from Anthropic and ChatGPT from OpenAI.
“I wanted to write a book that would help people better understand the new ways power manifests itself,” Colamedici told Decrypt.
But it wasn’t until after an investigative report from L’Espresso that Xun’s website was updated to acknowledge the experiment, snapshots from Wayback Machine reviewed by Decrypt show.
Still, the book received critical acclaim.
L’Espresso reports that L’Opinion, a French daily, had detailed how President Emmanuel Macron had “appreciated” Xun’s writings. Earlier in February, a roundtable at the World AI Cannes Festival extensively discussed Xun’s ideas.
Éditions Gallimard, a leading French publisher, has committed to a new translation from the Italian original, after the first edition in French from Philosophie Magazine. A Spanish translation from Editorial Rosamerón is slated for release on April 20.
Vibe philosophy?
Xun was “an exercise in ontological engineering,” Colamedici explained in a post-revelation interview with Le Grand Continent.
While this experiment with AI looked novel, critics point out the book could be in trouble.
The European Union’s AI Act, approved in March 2024, considers failure to label AI-generated content a serious violation – a requirement critics claim Colamedici’s experiment disregarded.
In previous versions of its bio, Xun was described as a “Hong Kong-born cultural analyst and philosopher” who studied at “Dublin University.”
That wasn’t true.
According to an anonymous source from the University College of Dublin’s philosophy department, no person named “Jianwei Xun” exists in their database or those of other Dublin-based universities.
“The fact that the author had inverted the Chinese order ‘surname-name’ was an immediate red flag,” Laura Ruggieri, a Hong Kong-based researcher, told Decrypt, explaining how she spotted inconsistencies as early as February.
Ruggieri previously taught semiotics—the study of symbols and signs—at the Hong Kong Polytechnic University. She asked her colleagues about Xun. Nobody knew who that was.
“Not a single one of them has ever met Xun or heard his name,” Ruggieri said. “If Colamedici had used his real name and admitted that AI had written the book, no one would have bought it.”
Responding to those allegations to Decrypt, Colamedici claimed these were deliberate clues “left for those willing to question and investigate,” claiming the revelation was “predetermined.”
“We actually did everything possible to make Xun’s non-existence evident to anyone with even minimally inquisitive eyes,” Colamedici said.
Colamedici insists that AI did not write the book. Instead, Claude and ChatGPT “served as interlocutors.”
In the words of Xun
The book describes itself as a “journey into the fractured mirror of modern reality,” and discusses how Musk and Trump have constructed an alternate reality through obsessive repetition.
It was written “for those who suspect that the world they see is only a shadow of something far more complex,” its Amazon blurb claims.
Xun’s thoughts center on “hypnocracy,” describing a regime that exerts control through “algorithmic modulation” of collective consciousness instead of censorship.
In English: fake news.
Xun claims that Trump’s speeches and social media posts create conditions of uncertainty.
Trump “empties language: his words, repeated endlessly, become empty signifiers, devoid of meaning yet charged with hypnotic power,” Xun wrote.
Xun claims Musk makes promises “destined not to materialize,” by “flooding our imagination” with ventures such as space colonization and neural interfaces.
“Together they modulate desires, rewrite expectations, colonize the unconscious,” the AI philosopher wrote.
Spokepeople for Musk and Trump did not immediately respond to Decrypt’s request for comment.
Edited by Sebastian Sinclair
Generally Intelligent Newsletter
A weekly AI journey narrated by Gen, a generative AI model.
Source link

Apple Delists 14 Crypto Apps in South Korea Including KuCoin and MEXC Exchanges Amid Regulatory Crackdown

Athens Exchange Group eyes first onchain order book via Sui

Futureverse Acquires Candy Digital, Taps DC Comics and Netflix IP to Boost Metaverse Strategy
Court Grants Ripple And SEC’s Joint Motion To Suspend Appeal

AVAX Falls 2.1% as Nearly All Assets Trade Lower

What is a VTuber, and how do you become one in 2025?

Top Expert’s Update Sets $10 Target

How Academia Interacts With The Bitcoin Ecosystem

AB DAO and Bitget Launch Dual Reward Campaign, Distributing $2.6M Worth of $AB Globally

AI crypto tokens at risk as Nvidia faces restrictions on China exports

Coinbase Urges Australia to Vote for Crypto Progress in May

How High Would Pi Network Price Go If Pi Coin Adopts Transparency to Avoid Mantra Pitfalls

XRP’s ‘Rising Wedge’ Breakdown Puts Focus on $1.6 Price Support

China selling seized crypto to top up coffers as economy slows: Report

Ethereum Price Dips Again—Time to Panic or Opportunity to Buy?

Arthur Hayes, Murad’s Prediction For Meme Coins, AI & DeFi Coins For 2025

Expert Sees Bitcoin Dipping To $50K While Bullish Signs Persist

Aptos Leverages Chainlink To Enhance Scalability and Data Access

Bitcoin Could Rally to $80,000 on the Eve of US Elections

Crypto’s Big Trump Gamble Is Risky

Sonic Now ‘Golden Standard’ of Layer-2s After Scaling Transactions to 16,000+ per Second, Says Andre Cronje

Institutional Investors Go All In on Crypto as 57% Plan to Boost Allocations as Bull Run Heats Up, Sygnum Survey Reveals

Ripple-SEC Case Ends, But These 3 Rivals Could Jump 500x

3 Voting Polls Show Why Ripple’s XRP Price Could Hit $10 Soon

Has The Bitcoin Price Already Peaked?

A16z-backed Espresso announces mainnet launch of core product
The Future of Bitcoin: Scaling, Institutional Adoption, and Strategic Reserves with Rich Rines

Xmas Altcoin Rally Insights by BNM Agent I

Blockchain groups challenge new broker reporting rule

I’m Grateful for Trump’s Embrace of Bitcoin
Trending

 24/7 Cryptocurrency News5 months ago
24/7 Cryptocurrency News5 months agoArthur Hayes, Murad’s Prediction For Meme Coins, AI & DeFi Coins For 2025

 Bitcoin3 months ago
Bitcoin3 months agoExpert Sees Bitcoin Dipping To $50K While Bullish Signs Persist

 24/7 Cryptocurrency News3 months ago
24/7 Cryptocurrency News3 months agoAptos Leverages Chainlink To Enhance Scalability and Data Access

 Bitcoin5 months ago
Bitcoin5 months agoBitcoin Could Rally to $80,000 on the Eve of US Elections

 Opinion5 months ago
Opinion5 months agoCrypto’s Big Trump Gamble Is Risky

 Altcoins3 months ago
Altcoins3 months agoSonic Now ‘Golden Standard’ of Layer-2s After Scaling Transactions to 16,000+ per Second, Says Andre Cronje

 Bitcoin5 months ago
Bitcoin5 months agoInstitutional Investors Go All In on Crypto as 57% Plan to Boost Allocations as Bull Run Heats Up, Sygnum Survey Reveals
 Price analysis5 months ago
Price analysis5 months agoRipple-SEC Case Ends, But These 3 Rivals Could Jump 500x


