Markets
Bitcoin’s Role as Collateral in Real Estate Development Financing
Published
4 months agoon
By
admin

Enhancing Creditworthiness with Bitcoin in a Debt-Intensive Economy
Since US President Richard Nixon announced in 1971 that the US dollar would no longer be convertible into gold at a fixed rate, central banks around the world have started operating a fiat-based monetary system with floating exchange rates and no currency standard. As a result, the money supply worldwide has increased exponentially and most industries now rely on credit to finance their operations and growth.
With the anticipated further devaluation of fiat currencies, driven by nation states needing to produce additional currency to cope with high borrowing costs, the creditworthiness of companies across all sectors is becoming increasingly important. This is particularly true for the real estate sector, which is extremely debt-intensive. In this context, bitcoin can play a crucial role as a disinflationary money, meaning its inflation rate decreases over time, providing an appreciating capital base that can help mitigate the risks associated with fiat currency devaluation and enhance a real estate company’s creditworthiness. In the following I will explain why bitcoin should be integrated into real estate development financing, illustrating how to integrate bitcoin into real estate investment from the start.
Why Bitcoin Should Be Integrated into Real Estate Development Financing
Real estate has been widely used as an inflation hedge since the inflationary policies following the Nixon shock in 1971, closely tracking the growth of the US money supply M2. Consequently, real estate has accrued a substantial monetary premium, indicative of the collective confidence in its ability to serve as a reliable store of value, a function traditionally associated with money, that is no longer possible due to decades of monetary inflation that has decimated fiat money’s purchasing power. However, with the rise of bitcoin, a near-perfect digital alternative, there’s potential for a shift. This gradual transition could diminish the monetary premium that real estate has historically enjoyed, redirecting it toward bitcoin over time. Bitcoin offers an alternative that is easier to access and cheaper to store and maintain.
Real estate investors can benefit greatly from integrating the purchase of bitcoin at the start of a development project by including it in project financing. This approach hedges against the scenario where real estate loses its monetary premium to bitcoin, due to bitcoin’s superior qualities as a store of value.
Similarly, bitcoin competes with real estate by serving as a digitally accessible, globally usable, and pristine collateral for lending. The popularity of real estate investments stems not only from its use as a store of value but also from its common use as collateral in the traditional banking system.
We can therefore assume that bitcoin’s increasing use as collateral, due to its accessibility and user-friendly nature for both borrowers and lenders, will negatively impact the use of real estate in this capacity. As more people recognize bitcoin’s advantages as collateral, real estate may see a decline in use for this purpose, while bitcoin’s importance as a type of collateral grows.
It is therefore important to integrate bitcoin into real estate development from the start, ensuring that investors are well-positioned to capitalize on bitcoin’s growing role in the financial landscape and its impact on real estate’s valuation.
My proposition is to integrate the purchase of bitcoin into real estate development financing. Allocating a portion of a loan, let’s say 10%, to purchase bitcoin enables real estate developers to hedge against the risk of real estate losing its status as humanity’s primary store of value. This strategy prepares real estate developers for a potential shift towards a Bitcoin standard, a hypothetical reality in which bitcoin becomes the world’s main store of value and unit of account, and real estate may no longer dominate.
The Benefits of Integrating Bitcoin into Real Estate Development Financing
By incorporating the purchase of bitcoin into real estate development financing and holding the bitcoin within the same legal entity that holds the property titles, developers can capture the monetary premium that flows from real estate into bitcoin, hedge against monetary inflation, and build resilience and creditworthiness over time. This ensures the ongoing viability of their business operations while leveraging the benefits of both asset classes: bitcoin’s price appreciation and real estate’s cash flow.
Integrating bitcoin into real estate financing can also help facilitate a smoother and more productive transition onto a Bitcoin standard where the value of real estate is expected to be based on its utility, as people can save in bitcoin by default rather than having to invest in real estate to protect their purchasing power. Additionally, this approach can help developers gain more independence from the inflationary fiat system, which is making it increasingly difficult to beat inflation and remain profitable.
Inflation severely devalues fiat currencies and erodes purchasing power. Initially, this scenario benefits the real estate sector as people invest in properties to outperform inflation, thus increasing its nominal value. Besides, inflation decreases the real cost of debt incurred to develop or purchase real estate over time, temporarily benefiting property owners. However, in the long term, inflation negatively affects the real estate industry due to soaring construction and maintenance costs, and the diminishing value of income generated from properties.
This dual impact underscores the need for an alternative strategy, such as incorporating bitcoin into credit products to hedge against the negative consequences of inflation. An ideal scenario for integrating bitcoin into real estate development would involve a financial service provider offering traditional financing supplemented with a portion of bitcoin in the loan. By incorporating the purchase of bitcoin into credit lines, businesses can not only survive but also thrive in an inflationary environment.
This approach benefits the borrower by providing a hedge against inflation but also offers the lender additional security through the inclusion of a disinflationary digital asset, bitcoin, as collateral.
I will now provide an example of such a loan.
Example Real Estate Development Loan Enhanced with Bitcoin
Let’s imagine a bank financing a $10 million real estate development project. The bank could extend the loan to $11 million and require the developer to purchase bitcoin for an additional $1 million, bringing the total loan amount to $11 million (with 91% intended for real estate development and 9% for bitcoin acquisition). This strategy serves as a hedge against several key risks for the borrower:
- It protects against the erosion of the monetary premium traditionally associated with real estate by the growing importance of bitcoin, a near-perfect digital store of value.
- It provides a safeguard against the perils of monetary inflation.
- It allows a company to build a novel capital base through the increase in value of bitcoin, which can be used to finance maintenance, further construction or other development projects.
- By owning bitcoin, particularly in the debt-intensive real estate sector, the credit rating of a company improves over time.
- Bitcoin, as an absolutely scarce and decentralized asset, exists outside the inflationary fiat system, offering stability during times of economic instability. In chaotic conditions, its limited supply and independence from central banks make its value proposition more apparent, acting as a hedge against financial collapse and strengthening the market from within.
- The borrower should ideally retain possession of the bitcoin for the long term and continuously, even after the loan is repaid. This serves as a hedge against property confiscation.
- Repeat the process with a new construction project while lending against the held bitcoin and potentially acquire more bitcoin through a new project financing, to continuously ensure the financial stability and growth of your business.
Including the purchase of bitcoin in a credit line also holds significant advantages for the lender. In the event of a project’s failure and subsequent property liquidation, both the lender and, depending on the agreement, ideally also the borrower, are left with an asset: bitcoin.
This principle is not limited to the real estate sector but is applicable to all industries. I can therefore imagine bitcoin becoming an integral part of credit products, specifically to hedge against loan defaults.
If bitcoin is properly secured, its purchasing power will continue to increase even in the event of a loan default. Bitcoin safeguards lenders and potentially borrowers in the event of a borrower’s failure to repay, provided that the borrower also holds custody of the bitcoin.
Including bitcoin in a loan not only acts as an effective hedge against default but also offers the advantage of swift and cost-effective liquidation in the event of non-payment. Bitcoin’s high liquidity considerably accelerates and reduces the expense of this process compared to a property. Once financial institutions understand that they can use bitcoin in this manner, it will undoubtedly become a fundamental component of lending solutions
Managing bitcoin custody properly is crucial. Consider multisignature setups or multi-custodial solutions to ensure security and control. For lending purposes, non-custodial solutions are emerging as a secure method for handling funds. Multisignature wallets, which require multiple signers to move funds, offer a significant advantage by allowing both lenders and borrowers to share custody. This collaborative approach enhances security and trust, as it provides oversight and control to all parties involved. It ensures that funds can only be accessed with the agreement of a majority of all authorized signers, reducing the risk of loss, theft, misuse, or mismanagement.
Conclusion
Including the purchase of bitcoin as part of a credit line generally increases the security of a loan structure, benefiting both borrowers and lenders. Bitcoin can be integrated relatively easily into the structure of real estate development financing. It presents a compelling narrative that challenges traditional views on real estate but offers an innovative solution to growing concerns about inflation and the rising costs of construction and maintenance.
The integration of bitcoin into financing is in its nascent stages, with no known products specifically tailored for real estate development. Nevertheless, the possibilities are vast and promising. This type of product will likely emerge from an innovative company that recognizes the potential of incorporating bitcoin into lending products. Traditional financial institutions are likely to be the last to recognize and seize this opportunity because of their reliance on established systems and regulatory constraints.
The dynamics described are prevalent in most industries, including real estate, banking and finance, energy, manufacturing, retail, healthcare, technology, aviation, mobility, food and beverages, and many others. Consequently, the integration of bitcoin into credit products would be beneficial to most industries, making it conceivable that bitcoin will become an integral part of credit markets, especially to secure loans against default. This could bolster the resilience of market actors in the face of rising economic and geopolitical uncertainties.
By embracing bitcoin-backed credit products, we can usher in a new era of economic empowerment and stability, with the potential to lead to greater resilience and productivity in the global economy.
This is a guest post by Leon Wankum. Opinions expressed are entirely their own and do not necessarily reflect those of BTC Inc or Bitcoin Magazine.
Source link
You may like

Most Layer 2 solutions are still struggling with scalability


Here’s why Stellar Price Could Go Parabolic Soon
Perp-Focused HyperLiquid Experiences Record $60M in USDC Net Outflows


Experts say these 3 altcoins will rally 3,000% soon, and XRP isn’t one of them


Robert Kiyosaki Hints At Economic Depression Ahead, What It Means For BTC?


BNB Steadies Above Support: Will Bullish Momentum Return?
Crypto exchange
Perp-Focused HyperLiquid Experiences Record $60M in USDC Net Outflows
Published
1 hour agoon
December 23, 2024By
admin
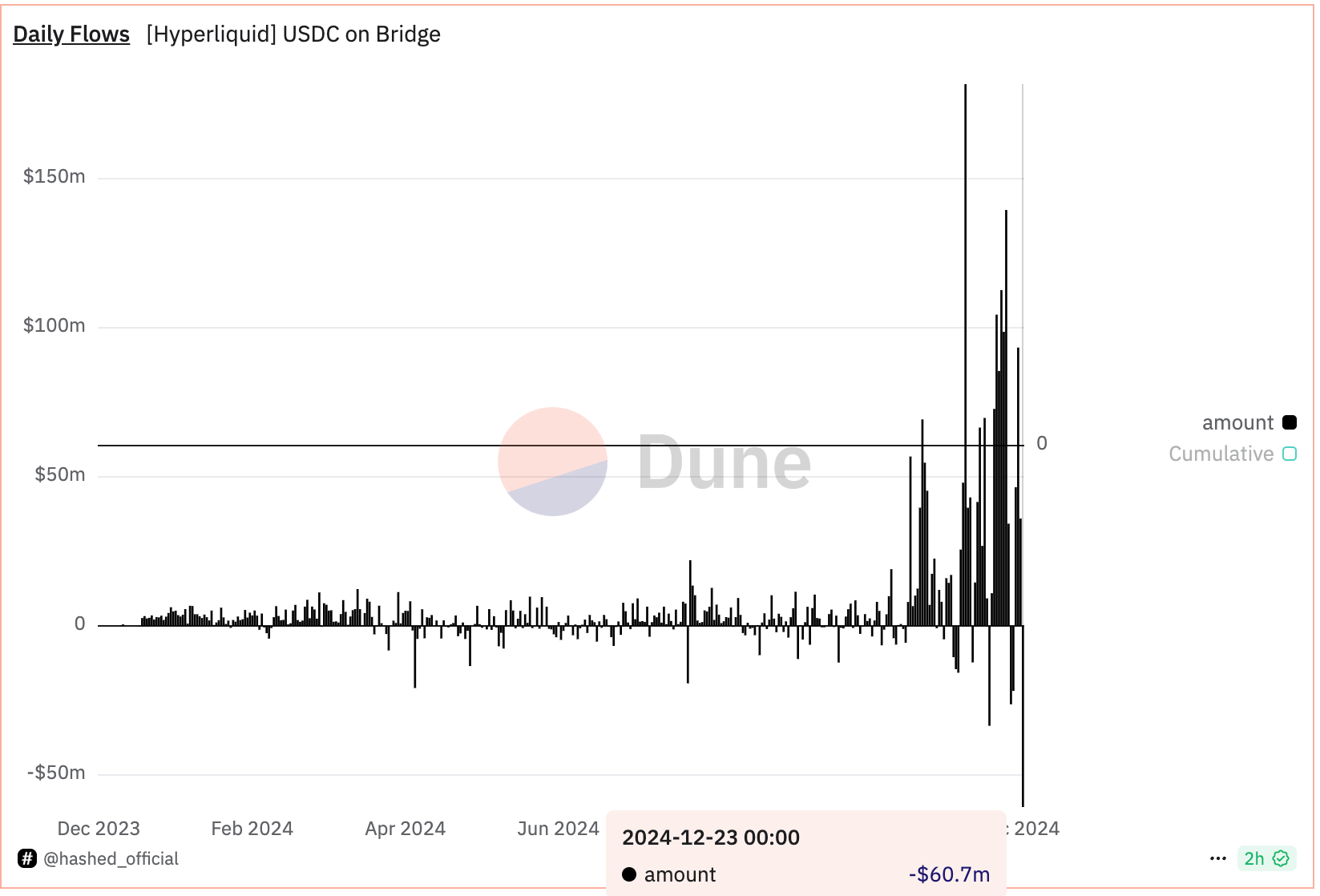
HyperLiquid, a layer-1 blockchain and decentralized exchange for perpetual futures (perps), has experienced a notable outflow of the USDC stablecoin amid speculation North Korean hackers are interacting with the platform, according to a post on X by pseudonymous observer Tay, known for tracking threats posed by to crypto protocols by the country.
A record $60 million of USDC fled the exchange by 10:00 UTC Monday, according to Hashed Official’s Dune-based tracker. USDC, the world’s second-largest dollar-pegged stablecoin, is used as collateral on HyperLiquid. The deposit bridge still holds $2.2 billion in USDC.
Addresses associated with hackers from the Democratic People’s Republic of Korea (DPRK) have accrued losses exceeding $700,000 while trading on HyperLiquid, Tay said. The transactions indicate the hackers are potentially familiarizing themselves with the platform’s inner workings to launch a malicious attack.
“DPRK doesn’t trade. DPRK tests,” Tay said.
CoinDesk contacted HyperLiquid on X for comments on the USDC outflows and potential threat from North Korea.
Tay said they reached out to the platform two weeks ago, offering help in countering a potential threat.
“I really want to emphasize that these are the most sophisticated and rapidly evolving of all of the DPRK threat groups. They are very creative and persistent. They also get their hands on 0days (such as the one Chrome patched today,” Tay’s message to the platform said.
HyperLiquid is the leading on-chain perpetuals exchange, commanding over 50% of the total on-chain perpetuals trading volume, which tallied $8.6 billion in the past 24 hours.
The platform debuted its token HYPE on Nov. 29. Since then, it has
surged over 600% to $28.6, briefly topping $10 billion in market capitalization. As of writing, HYPE was the 22nd largest digital asset in the world, according to Coingecko.
Source link
DeFi
DeFi Protocol Usual’s Surge Catapults Hashnote’s Tokenized Treasury Over BlackRock’s BUIDL
Published
17 hours agoon
December 22, 2024By
admin
There’s been a change of guard at the rankings of the $3.4 billion tokenized Treasuries market.
Asset manager Hashnote’s USYC token zoomed over $1.2 billion in market capitalization, growing five-fold in size over the past three months, rwa.xyz data shows. It has toppled the $450 million BUIDL, issued by asset management behemoth BlackRock and tokenization firm Securitize, which was the largest product by size since April.

USYC is the token representation of the Hashnote International Short Duration Yield Fund, which, according to the company’s website, invests in reverse repo agreements on U.S. government-backed securities and Treasury bills held in custody at the Bank of New York Mellon.
Hashnote’s quick growth underscores the importance of interconnecting tokenized products with decentralized finance (DeFi) applications and presenting their tokens available as building blocks for other products — or composability, in crypto lingo — to scale and reach broader adoption. It also showcases crypto investors’ appetite for yield-generating stablecoins, which are increasingly backed by tokenized products.
USYC, for example, has greatly benefited from the rapid ascent of the budding decentralized finance (DeFi) protocol Usual and its real-world asset-backed, yield-generating stablecoin, USD0.
Usual is pursuing the market share of centralized stablecoins like Tether’s USDT and Circle’s USDC by redistributing a portion of revenues from its stablecoin’s backing assets to holders. USD0 is primarily backed by USYC currently, but the protocol aims to add more RWAs to reserves in the future. It has recently announced the addition of Ethena’s USDtb stablecoin, which is built on top of BUIDL.
“The bull market triggered a massive inflow into stablecoins, yet the core issue with the largest stablecoins remains: they lack rewards for end users and do not give access to the yield they generate,” said David Shuttleworth, partner at Anagram. “Moreover, users do not get access to the protocol’s equity by holding USDT or USDC.”
“Usual’s appeal is that it redistributes the yield along with ownership in the protocol back to users,” he added.

The protocol, and hence its USD0 stablecoin, has raked in $1.3 billion over the past few months as crypto investors chased on-chain yield opportunities. Another significant catalyst of growth was the protocol’s governance token (USUAL) airdrop and exchange listing on Wednesday. USUAL started trading on Binance on Wednesday, and vastly outperformed the shaky broader crypto market, appreciating some 50% since then, per CoinGecko data.
BlackRock’s BUIDL also enjoyed rapid growth earlier this year, driven by DeFi platform Ondo Finance making the token the key reserve asset of its own yield-earning product, the Ondo Short-Term US Government Treasuries (OUSG) token.
Source link
Markets
Chainlink price double bottoms as whales accumulate
Published
21 hours agoon
December 22, 2024By
admin
Chainlink formed a double-bottom pattern, pointing to a potential rebound, as signs showed that some whales were accumulating the token.
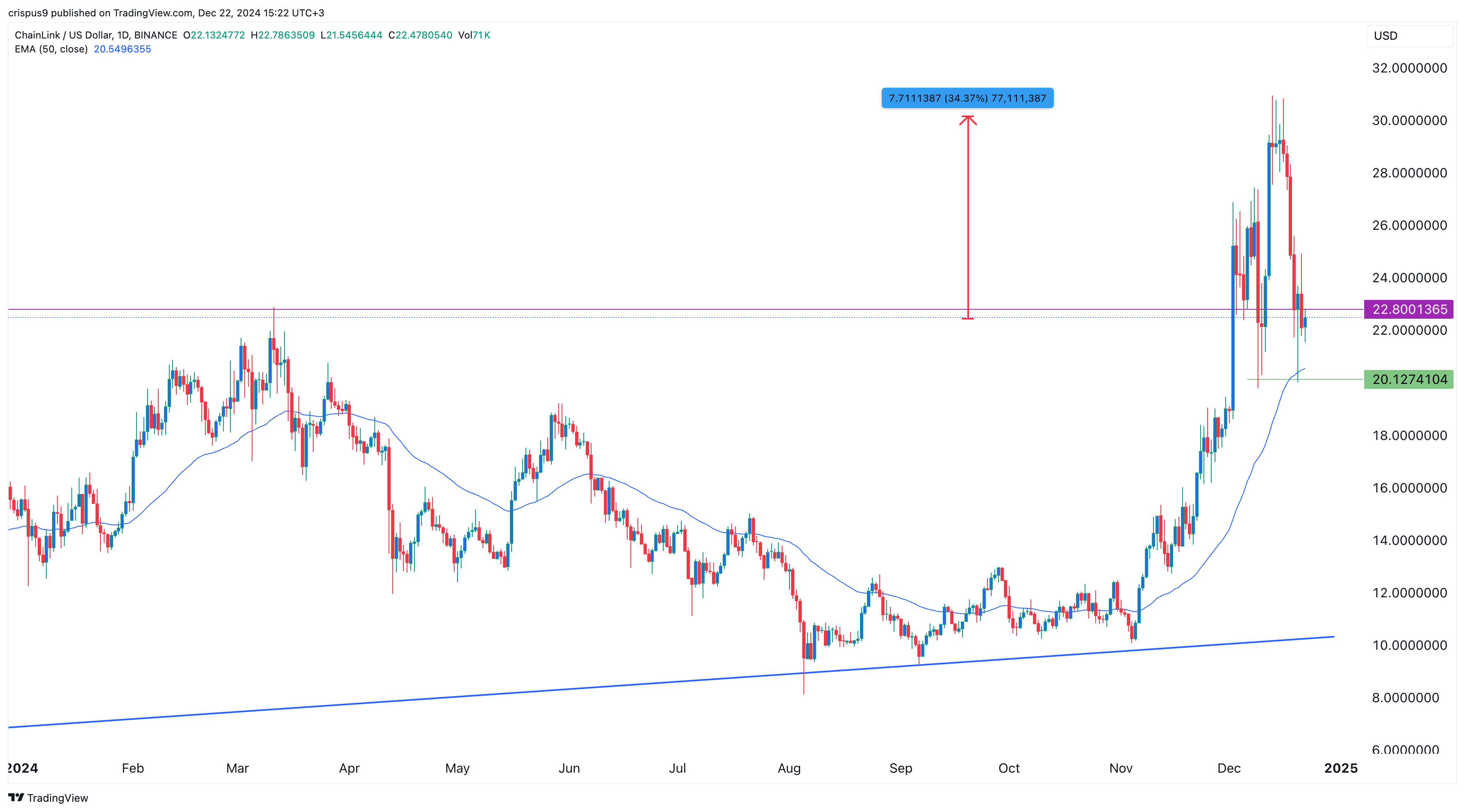
Chainlink (LINK), the biggest oracle provider, bottomed at $20.12 on Friday and rebounded to $22.50 on Sunday, Dec. 22. Still, the coin remains about 27% from its highest point this month, meaning that it is in a bear market.
A potential catalyst for the LINK token is that whales are accumulating it. According to LookOnChain, nine new wallets withdrew 362,380 coins from Binance in the last two days. These coins are now valued at over $8.19 million.
Crypto.news reported last week that another whale accumulated 65,000 LINK coins valued at $1.8 million.
Whales are accumulating $LINK!
We noticed 9 fresh wallets that withdrew 362,380 $LINK($8.19M) from #Binance in the last 48 hours.
Address:
0xdA44049389F87c1170C5e7319c9eb93acDf83304
0xC10396589a40438CcdF48bA1b2061a6067DAa972
0x5199b3Ce02a912056ea8A460371aD83020693F6C… pic.twitter.com/vpAMR0dhbd— Lookonchain (@lookonchain) December 22, 2024
These whales bought Chainlink a week after World Liberty Financial (WLFI), the DeFi platform launched by the Trump family, bought over 78,300 LINK tokens valued at over $1.7 million. It’s worth noting that President-elect Trump and his family mostly own WLFI tokens.
Chainlink, known in the crypto industry for its fundamentals, is the biggest oracle in the sector with over $35 billion in total value secured. That figure is higher than its biggest competitors like Chronicle, Pyth, Edge, and Redstone.
Chainlink’s ecosystem will likely grow as more chains and networks embrace its technology. Justin Sun’s Tron, the most recent chain to use its oracles, has switched from WINKLink to Chainlink.
Chainlink has also formed major partnerships in the Real World Asset tokenization industry, including by companies like Coinbase, Emirates NBD, SWIFT, and UBS.
Chainlink price formed a double-bottom pattern
LINK, like other cryptocurrencies, has dropped sharply in the past few days as concerns about the Federal Reserve remained.
The token has remained above the 50-day moving average on the daily chart. Most importantly, it has formed a double-bottom chart pattern at $20.12. This pattern happens when an asset fails to move below a specific price two times. It is one of the most bullish reversal patterns in the market.
LINK has also formed an inverse hammer pattern, a popular reversal sign. Therefore, the coin is likely to bounce back in the next few days as investors target the key psychological at $30, which is about 35% above the current level.
On the flip side, the bullish view will become invalid if the coin drops below the double-bottom point at $20.12.
Source link

Most Layer 2 solutions are still struggling with scalability

Here’s why Stellar Price Could Go Parabolic Soon

Perp-Focused HyperLiquid Experiences Record $60M in USDC Net Outflows

Experts say these 3 altcoins will rally 3,000% soon, and XRP isn’t one of them

Robert Kiyosaki Hints At Economic Depression Ahead, What It Means For BTC?

BNB Steadies Above Support: Will Bullish Momentum Return?

Metaplanet makes largest Bitcoin bet, acquires nearly 620 BTC

Tron’s Justin Sun Offloads 50% ETH Holdings, Ethereum Price Crash Imminent?

Investors bet on this $0.0013 token destined to leave Cardano and Shiba Inu behind

End of Altcoin Season? Glassnode Co-Founders Warn Alts in Danger of Lagging Behind After Last Week’s Correction

Can Pi Network Price Triple Before 2024 Ends?

XRP’s $5, $10 goals are trending, but this altcoin with 7,400% potential takes the spotlight

CryptoQuant Hails Binance Reserve Amid High Leverage Trading

Trump Picks Bo Hines to Lead Presidential Crypto Council

The introduction of Hydra could see Cardano surpass Ethereum with 100,000 TPS
182267361726451435

Why Did Trump Change His Mind on Bitcoin?

Top Crypto News Headlines of The Week

New U.S. president must bring clarity to crypto regulation, analyst says

Will XRP Price Defend $0.5 Support If SEC Decides to Appeal?

Bitcoin Open-Source Development Takes The Stage In Nashville

Ethereum, Solana touch key levels as Bitcoin spikes

Bitcoin 20% Surge In 3 Weeks Teases Record-Breaking Potential

Ethereum Crash A Buying Opportunity? This Whale Thinks So

Shiba Inu Price Slips 4% as 3500% Burn Rate Surge Fails to Halt Correction

Washington financial watchdog warns of scam involving fake crypto ‘professors’

‘Hamster Kombat’ Airdrop Delayed as Pre-Market Trading for Telegram Game Expands

Citigroup Executive Steps Down To Explore Crypto
Mostbet Güvenilir Mi – Casino Bonus 2024

NoOnes Bitcoin Philosophy: Everyone Eats
Trending

 3 months ago
3 months ago182267361726451435

 Donald Trump5 months ago
Donald Trump5 months agoWhy Did Trump Change His Mind on Bitcoin?

 24/7 Cryptocurrency News4 months ago
24/7 Cryptocurrency News4 months agoTop Crypto News Headlines of The Week

 News4 months ago
News4 months agoNew U.S. president must bring clarity to crypto regulation, analyst says

 Price analysis4 months ago
Price analysis4 months agoWill XRP Price Defend $0.5 Support If SEC Decides to Appeal?

 Opinion5 months ago
Opinion5 months agoBitcoin Open-Source Development Takes The Stage In Nashville

 Bitcoin5 months ago
Bitcoin5 months agoEthereum, Solana touch key levels as Bitcoin spikes

 Bitcoin5 months ago
Bitcoin5 months agoBitcoin 20% Surge In 3 Weeks Teases Record-Breaking Potential


