evm
BitReXe: Enabling Parallel VMs on Bitcoin Network
Published
4 weeks agoon
By
admin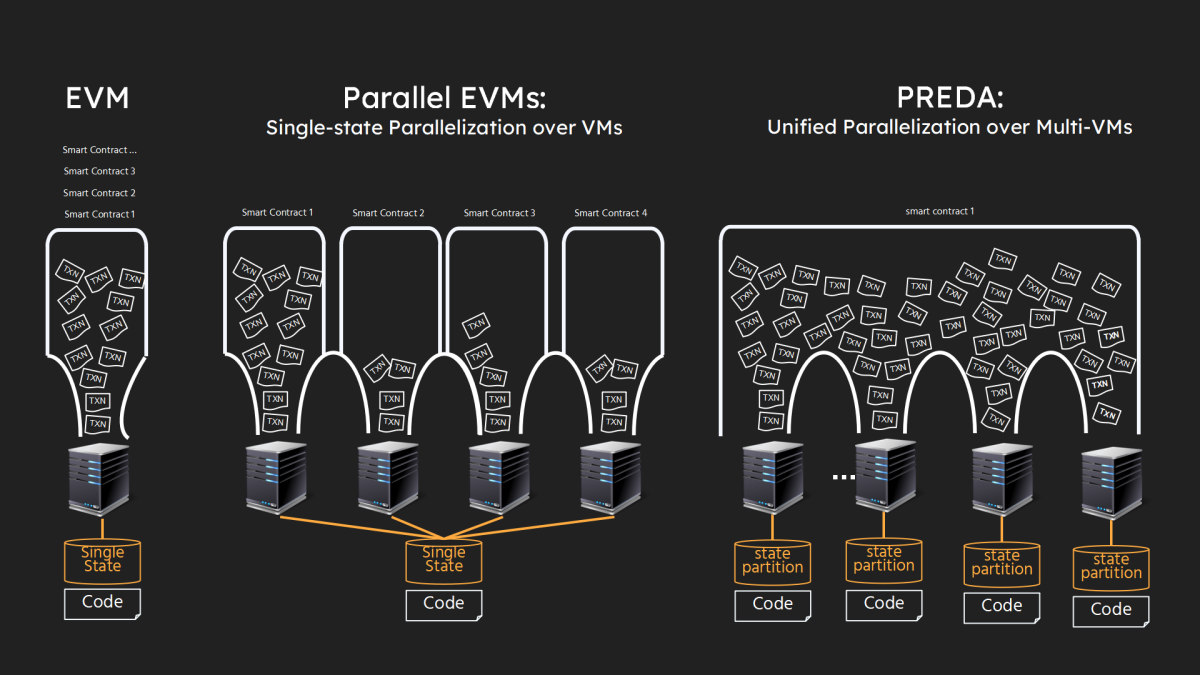
Ethereum is still working on a complementary plan for parallel EVM, but Bitcoin can be soon expecting its own parallel VM layer 2.
Let’s firstly understand why Ethereum cannot achieve parallel EVM.
To maintain network consistency and security, EVM has a crucial feature in its design: transactions are executed sequentially. Sequential execution ensures that transactions and smart contracts can be executed in a deterministic order, making it easier to manage and predict the blockchain’s state. This design choice prioritizes security, reducing potential complexities and vulnerabilities associated with parallel execution. However, under high loads of transaction requests, this sequential execution can lead to network congestion and delays, similar to a single-lane highway.
Is it feasible to simply add lanes? Referencing existing solutions of so-called parallel VMs, including sharding chains like Near. These chains proposed to scale blockchain by introducing more VMs to scale smart contracts. Essentially the workload of one smart contract still lies in a certain VM. If all smart contracts on this chain consume an equal amount of TPS, then the problem is solved. However, if only a few contracts, such as Aave and Uniswap protocols, consume over 90% of block space, having contracts running on a single shard means only scaling at the chain level without benefiting from the improvements brought by sharding. Adding lanes without the ability to switch lanes represents the current dilemma of parallelization of VMs.
The Parallel EVM involves cutting or caching data at the data layer. However, limited by EVM’s programming model, Solidity, as the most popular smart contract programming language, cannot maximize the potential of parallel blockchain architecture. It’s akin to not programming with SQL on NVIDIA’s GPU. Solidity lacks expressions for parallel architectures like Relay Execution and lacks a defined final atomicity for parallel transactions.
True parallelism in blockchain architecture requires achieving the result that transactions of one smart contract can run on multiple VMs simultaneously. A programming model like CUDA is needed to fully leverage a parallel model in blockchain architecture.
BitReXe mentions Bitcoin introduces Turing-complete parallel VM Layer 2 to provide underlying infrastructure support for real applications in the Bitcoin ecosystem and an exclusive programming model for parallel VMs, PREDA.
How BitReXe achieves Parallel Vms on Bitcoin
Parallel VMs
The following illustration highlights the distinctions between BitReXe and other initiatives promoting Parallel VMs. As shown in the leftmost segment of the figure, Ethereum adheres to a single-machine state model, wherein all codes (smart contracts) and states (data) are replicated and managed by each blockchain node through its Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM). The extant projects utilize Parallel EVMs, as shown in the middle section of the figure, where a single smart contract is deployed on a dedicated VM (or VMs within a designated shard to uphold consensus). All transactions pertaining to the smart contract are processed by the VM (or VMs of the shard in a fully duplicated manner).
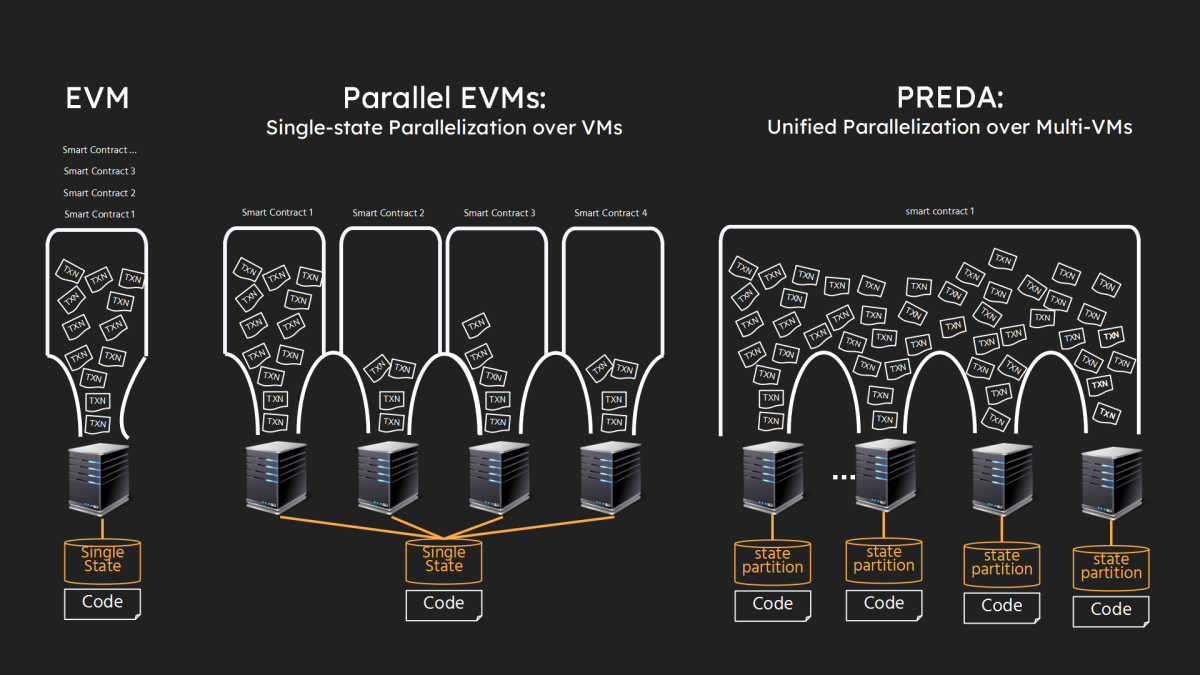
In BitReXe’s unified parallelization model, as shown in the rightmost segment of the figure, all smart contracts are deployed across all VMs of the network. The states of a smart contract undergo partitioning and distribution across distinct VM instances, ensuring non-overlapping allocation. Correspondingly, transactions of the smart contract are segmented and distributed for independent and parallel processing across VMs. In the ideal case, this approach facilitates a linear scaling of overall transaction throughput and state capacity with an increasing number of VMs.
The primary challenge lies in efficiently managing the dependencies between execution logic (code) and contract state (data) while enabling independent VM execution and avoiding synchronization, since the comprehensive execution logic of a transaction may entail access to multiple segments of contract states, each residing in separate VMs after state partitioning.
PREDA
We present Parallel Relay-Execution Distributed Architecture (PREDA), a groundbreaking programming model designed to scale out smart contracts on sharding blockchains, parachain systems, and layer-2 blockchains. PREDA supports a parallel architecture: if Solidity for Ethereum is likened to program on a single-core CPU, PREDA’s parallel architecture for BitReXe is akin to CUDA for NVIDIA’s GPU.
The PREDA model introduces two key components: (1) “Programmable Contract Scopes”, enabling programmers to define contract state partitioning based on the application’s data access pattern, narrowing data access range and minimizing data dependency; and (2) “Asynchronous Functional Relay”, allowing programmers to articulate transaction logic with implicit data dependencies for flexible execution across multiple execution engines (VMs). Implemented as an extended Solidity language, PREDA includes additional syntax for programmable contract scopes and statements for asynchronous functional relay.
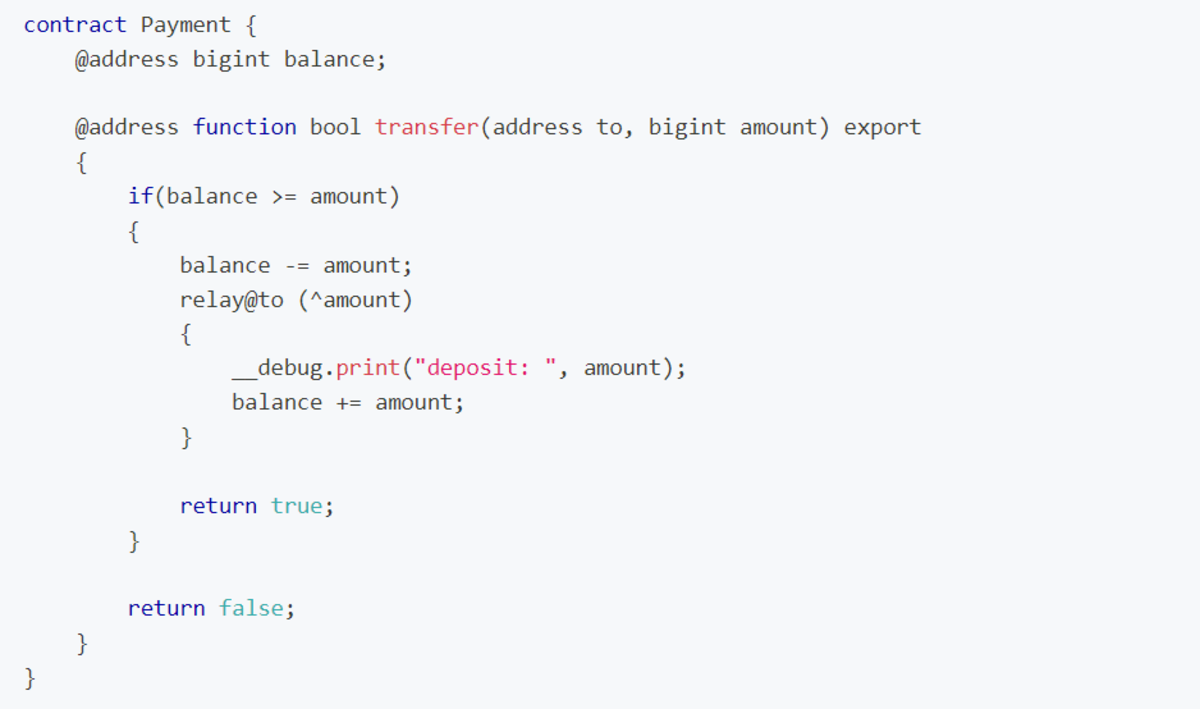
The figure illustrates the PREDA version of a simplified ERC20 contract. The “@address” keyword defines the scope of users’ balances, equivalent to Solidity’s map definition but specifies fine-grained and separable states for partitioning by address. At runtime, states partitioned by address are managed by a set of VMs in the BitReXe chain. Different states are not maintained by different sets of VMs. The transfer function within the “@address” scope, invoked by payers (i.e., user addresses initiating transfer transactions), initiates a ” relay” for depositing to the payee. This relay, executed by a VM hosting the payee’s address states, adds funds to the payee’s balance.
In PREDA, a smart contract can have multiple scopes with variables and functions defined. Multiple functions and variables of arbitrary types including containers can be defined in a scope. Multiple relays, conditionally or unconditionally, can be initiated in a single function call, allowing recursive initiation and enabling transaction execution flow to be moved multi-hops across different VM instances. This relay-execution approach decomposes a transaction into multiple Micro-Transactions, ensuring limited state access in a single virtual machine and avoiding race conditions. In the PREDA transfer smart contract, decomposing the transaction into a “withdraw” micro-transaction and a “deposit” micro-transaction enables parallel execution of these two types of micro-transactions, as long as their targets (addresses in this case) are mapped to different virtual machines.
BitReXe organizes virtual machines into multiple consensus groups, each independently running a consensus protocol (PoW-based in the implementation) to reach consensus on executed transactions. Across-group consensus is implemented to maintain correctness and consistency for asynchronous functional relays, implemented as relay transactions in BitReXe.
Bitcoin Layer 2
Asset issuance paradigm on Bitcoin layer like inscription is constantly exploiting a vulnerability in Bitcoin, says Luke. While money never sleeps, just as inscriptions may never die. Bitcoin is in desperate need of a truly scalable layer 2 that can release such pressure and save the ledger size from growing too fast which will weaken the decentralization. Such a goal is very unlikely to be achieved by an EVM+Bridge solution.
BitReXe proposes Parallel VMs and PREDA to scale bitcoin. Meanwhile, it adapts to the security of bitcoin. It uses BTC as gas fee, shares the security of Bitcoin, and provides a trustless asset settlement between the two chains.
BitReXe reuses hashing computing power by the Bitcoin network which is carried by on-chain blocks, orphan blocks, and premature blocks as proof-of-work to create valid blocks in the layer-2 network without modifying the Bitcoin protocol. Merge miners receive rxBTC as rewards, a 1:1 pegged bitcoin on the BitReXe network. Users pay gas fees with rxBTC for transactions, interacting with smart contracts, and other on-chain activities. Fullnodes lab, the dev team of PREDA and BitReXe is about to introduce a trustless asset settlement bridge solution between Bitcoin and BitReXe, where rxbtc peg-out is at the same time someone’s BTC peg-in. Official peg-out addresses are no longer required, thus trust assumption is therefore eliminated.
Our high expectations for the Bitcoin ecosystem stem from its ability to solve problems that Ethereum – as Bitcoin’s testnet – has not addressed.
@Bit_ReXe believes that this issue stems from EVM lacking parallel mechanisms leading to blockchain trilemma and aims to directly solve it on Bitcoin Layer 2.
If this issue can be resolved on Bitcoin, then TVL benchmarking or even surpassing Ethereum by more than three times on Bitcoin Layer 2 would present a fundamental breakthrough.”
This is a guest post by BitPNova. Opinions expressed are entirely their own and do not necessarily reflect those of BTC Inc or Bitcoin Magazine.
Source link
You may like


Multicoin Capital pledges up to $1m to pro-crypto Senate candidates


MATIC Price Crash: Reaching A Two Year Low


Multicoin Pledges up to $1M for Pro-Crypto Senate Candidates


Crypto heists near $1.4b in first half of 2024: TRM Labs


FTX Founder Sam Bankman-Fried’s Family Accused Of $100M Illicit Political Donation


Bitcoin Price Falls as Mt Gox Starts Repayments
Bitcoin
Protocol Village: Farworld, Building Gaming on Farcaster, Raises $1.75M
Published
2 weeks agoon
June 20, 2024By
admin

The latest in blockchain tech upgrades, funding announcements and deals. For the period of June 20-26.
Source link
Bitcoin
Protocol Village: Synthetix Launches on Arbitrum, Adding to Chains Beyond Ethereum
Published
3 weeks agoon
June 18, 2024By
admin

The latest in blockchain tech upgrades, funding announcements and deals. For the period of June 13-19.
Source link
Bitcoin
Biconomy’s ‘Delegated Authorization Network’ for AI Agents Relies on EigenLayer
Published
3 weeks agoon
June 12, 2024By
admin
June 11: Biconomy, a Web3 infrastructure company, launched a new “Delegated Authorization Network,” or DAN, “enabling the safe delegation of on-chain activities to AI agents,” according to the team. A press release added: “Biconomy DAN operates by granting AI projects approved access to user’s ‘Delegated Auth’ keys stored on an EigenLayer AVS (Actively Validated Services), ensuring true autonomy without compromising on security. To integrate DAN into an AI agent, projects need to use key storage on DAN, an EigenLayer AVS, and program user-defined permissions for those keys using the DAN SDK. Biconomy has collaborated with Silence Labs for the development and launch of DAN.” A blog post is here.
:format(jpg)/cloudfront-us-east-1.images.arcpublishing.com/coindesk/N6GYM7MW4NEDJHCYSTHC2SLRAQ.png)
Ava Protocol Raises $10M for EigenLayer AVS for ‘Private Autonomous Transactions’
June 11: Ava Protocol, formerly OAK Network, secured $10 million in seed funding ($5.5 million initial and $4.5M seed+ rounds) to develop its Eigenlayer AVS for private autonomous transactions on Ethereum, according to the team: “Investors include Electric Capital, Taisu Ventures and Polygon founder Sandeep Nailwal. The funding supports core Web3 infrastructure, enabling cross-chain smart contract automation for applications like limit orders on decentralized exchanges. Over 10,000 wallets use its testnet with 1,000+ daily transactions. With 30+ partners, including Polkadot and Moonbeam, Ava aims to simplify Web3 application deployment.”
Covalent Says Arthur Hayes to Advise on Development of ‘Ethereum Wayback Machine’
June 11: Covalent, provider of a decentralized network for indexing blockchain data, announced that BitMEX founder Arthur Hayes has been named as a new strategic advisor. Hayes, who currently serves as chief investment officer of Maelstrom, “will be leading the development of the Ethereum Wayback Machine, ensuring that all Ethereum and EVM rollup data will shape AI with a preformat and verifiably secure pipeline,” according to the team. “This partnership will further secure Ethereum’s historical data preservation, ensuring accessibility and transparency to the ecosystem’s full history.”
Overlai, Blockchain Project for Image Verification, Launches Mobile App, Adobe Plugin on Aptos
June 11: Overlai, a blockchain project for image verification co-founded by photographers Paul Nicklen and Cristina Mittermeier, announced the beta launch of its mobile app and Adobe Plugin on Aptos. according to the team: “After validating a picture in Overlai – a process that can be completed in just a few clicks – creators can upload the asset to any digital medium and retain full ownership. No matter how much the photo is screenshotted, compressed, or converted, Overlai’s invisible watermark with a creator’s credentials, securely stored on the Aptos blockchain, stays intact – answering a pressing need amid the rise of generative AI.” (APT)
Vana, Network for User-Owned Data, Releases Satori Testnet
June 11: Vana, a network for user-owned data, released its Satori testnet. “Users can now mine and contribute to the network by exporting their data from platforms, leveraging data rights to sidestep big tech’s walled gardens. Proof-of-contribution ensures data quality by rewarding users proportionally to their data’s impact on AI model performance,” according to a blog post.
Flock.io, Ritual Form Partnership to Advance ‘Decentralized AI Composability’
June 11: FLock.io, a project to decentralize machine learning for AI models, and Ritual, which enables developers to access models on-chain via smart contracts, announced a strategic partnership to advance decentralized AI composability. According to the team: “Leveraging Ritual’s Infernet nodes, FLock.io aims to enhance transparency and verifiability in task routing, model usage and rewards distribution within the decentralized AI ecosystem. This collaboration underscores a commitment to fostering a fair and open-source environment where developers and contributors are compensated based on model usage.”
Core, EVM-Compatible L1 Aligned With Bitcoin, Launches Hackathon
June 11: Core, an Ethereum-compatible layer-1 blockchain project that relies on Bitcoin for its security setup, “is launching the BTCfi Summer Hackathon, a 12-week event designed to ignite innovation in the Bitcoin economy,” according to the team: “There are prizes for the top three positions ranging from a $5,000 – $15,000 grant, access to Defi workshops, social media highlights, a feature in the BTCfi ecosystem newsletter and more. The hackthon launched June 6 and the winners will be announced Aug. 19.”
Polygon Creates New Grants Program, 1B POL Unlocked Over 10 Years
June 11: Layer-2 network Polygon is starting a Community Grants Program to encourage builders to build in its ecosystem, Polygon Labs said on Tuesday. The program aims to place 1 billion POL, Polygon’s soon-to-rebrand MATIC token, into the hands of developers over the next 10 years. The program went live Tuesday with 35 million tokens, worth $23 million at current prices, eligible for distribution. The network is in the process of transitioning its current token, MATIC, to the new POL ticker, so this first tranche of tokens will be denominated in MATIC.
SubQuery Network, for Decentralized Indexers, Launches RPCs for Polkadot, Kusama
June 11: SubQuery Network, a distributed network of decentralized indexers and RPC providers, is launching the first decentralized RPCs for Polkadot and Kusama, according to the team: “The Polkadot RPCs that have been deployed for the Polkadot relay chain and Kusama are operated by more than 30 independent node operators.”
Optimism Finally Gets Its Mission-Critical ‘Fault Proofs’
June 11: Until now, the Ethereum layer-2 project Optimism has been missing a core feature at the heart of its security design: “Fault proofs.” On Monday, that long-promised tech finally came to Optimism’s mainnet. The Optimism team previously shared in March that it was testing its fault proofs system on their Sepolia testnet. Since then, they had an audit conducted by blockchain security firm Sherlock, and found a few bugs that they were able to patch out. “We literally deleted the entire system essentially, re-architected it, and rewrote the entire thing,” Karl Floersch, the CEO of OP Labs, said in an interview with CoinDesk.
Cardano Is on Track for Voltaire Upgrade This Month, Co-Founder Hoskinson Says
June 11: The Cardano network is set to move into the final phase of a multiyear program to become a wholly decentralized blockchain ecosystem later this month, co-founder Charles Hoskinson said in an X post Monday. As a first step, the validating node software operated by the system’s stake pool operators, or SPOs, needs to be upgraded to the latest version. Then, the blockchain will evolve into a backward-incompatible version, a process known as a hard fork, and in doing so, enter a new era known as Voltaire. Once the switch is complete, the seven-year-old blockchain will no longer be actively managed by Cardano development firm IOHK, instead wholly run by community members, according to a project roadmap. (ADA)
Lido Introduces ‘Restaking Vaults’ in Collaboration with Symbiotic, Mellow Finance
June 11: A new initiative from Lido DAO will see Lido’s partnering with Mellow Finance, a platform that lets users generate yield by depositing into restaking “vaults,” and Symbiotic, a permissionless restaking protocol. Mellow curators Steakhouse, P2P Validator, Re7 Labs and MEV Capital are each introducing vaults that accept stETH in tandem with Tuesday’s announcement. (LDO)
Protocol Village is a regular feature of The Protocol, our weekly newsletter exploring the tech behind crypto, one block at a time. Sign up here to get it in your inbox every Wednesday. Project teams can submit updates here. For previous versions of Protocol Village, please go here. Also please check out our weekly The Protocol podcast.
June 10: Wormhole, the blockchain interoperability protocol, will allow holders of its W token to stake with the Tally Governance Portal, “allowing the opportunity to participate in governance and influence the future direction of the Wormhole DAO and platform,” according to the team.” The update marks “a significant step toward decentralizing Wormhole through MultiGov, an industry-first multichain governance system for DAOs on Solana, Ethereum mainnet, and EVM L2s,” Wormhole said in a statement. “The Wormhole DAO will be the first to adopt MultiGov, enabling W holders to create, vote on, and execute governance proposals on any supported chain.”
Squads Labs Raises $10M Series A, Unveils Smart Wallet for Public Testing on iOS
June 10: Technology company Squads Labs, which aims to help businesses transact in and manage digital assets, raised $10 million in Series A funding led by Electric Capital. The funding round included participation from RockawayX, Coinbase Ventures, L1 Digital and Placeholder, Squads Labs said in an email on Monday. Squads has also unveiled a smart wallet aimed at individuals for public testing on iOS.
Edited by Sam Kessler and Bradley Keoun.
Source link

Multicoin Capital pledges up to $1m to pro-crypto Senate candidates

MATIC Price Crash: Reaching A Two Year Low

Multicoin Pledges up to $1M for Pro-Crypto Senate Candidates

Crypto heists near $1.4b in first half of 2024: TRM Labs

FTX Founder Sam Bankman-Fried’s Family Accused Of $100M Illicit Political Donation

Bitcoin Price Falls as Mt Gox Starts Repayments

20% Price Drop Follows $87 Million Spending Outrage

More than 10 years since the collapse of Mt. Gox, users confirm reimbursements

Leading Telecom Company Taiwan Mobile Gets Crypto Exchange License

Here Are Price Targets for Bitcoin, Solana, and Render, According to Analyst Jason Pizzino

Bitcoin price plunges below $55k as Mt. Gox announces repayments

Jasmy Sheds 20% Amid Bitcoin Sell-Off

Are they a good thing?

Mt. Gox Transfers $2.7 Billion in Bitcoin From Cold Storage Amid Market Rout

What’s Next For Ethereum (ETH) as Price Hovers $3,000?

Bitcoin Dropped Below 2017 All-Time-High but Could Sellers be Getting Exhausted? – Blockchain News, Opinion, TV and Jobs

What does the Coinbase Premium Gap Tell us about Investor Activity? – Blockchain News, Opinion, TV and Jobs
BNM DAO Token Airdrop

NFT Sector Keeps Developing – Number of Unique Ethereum NFT Traders Surged 276% in 2022 – Blockchain News, Opinion, TV and Jobs
A String of 200 ‘Sleeping Bitcoins’ From 2010 Worth $4.27 Million Moved on Friday
New Minting Services

Block News Media Live Stream

SEC’s Chairman Gensler Takes Aggressive Stance on Tokens – Blockchain News, Opinion, TV and Jobs

Friends or Enemies? – Blockchain News, Opinion, TV and Jobs

Enjoy frictionless crypto purchases with Apple Pay and Google Pay | by Jim | @blockchain | Jun, 2022

How Web3 can prevent Hollywood strikes

Block News Media Live Stream

Block News Media Live Stream

Block News Media Live Stream

XRP Explodes With 1,300% Surge In Trading Volume As crypto Exchanges Jump On Board
Trending

 Altcoins2 years ago
Altcoins2 years agoBitcoin Dropped Below 2017 All-Time-High but Could Sellers be Getting Exhausted? – Blockchain News, Opinion, TV and Jobs

 Binance2 years ago
Binance2 years agoWhat does the Coinbase Premium Gap Tell us about Investor Activity? – Blockchain News, Opinion, TV and Jobs
- Uncategorized3 years ago
BNM DAO Token Airdrop

 BTC1 year ago
BTC1 year agoNFT Sector Keeps Developing – Number of Unique Ethereum NFT Traders Surged 276% in 2022 – Blockchain News, Opinion, TV and Jobs

 Bitcoin miners2 years ago
Bitcoin miners2 years agoA String of 200 ‘Sleeping Bitcoins’ From 2010 Worth $4.27 Million Moved on Friday
- Uncategorized3 years ago
New Minting Services

 Video2 years ago
Video2 years agoBlock News Media Live Stream

 Bitcoin1 year ago
Bitcoin1 year agoSEC’s Chairman Gensler Takes Aggressive Stance on Tokens – Blockchain News, Opinion, TV and Jobs

